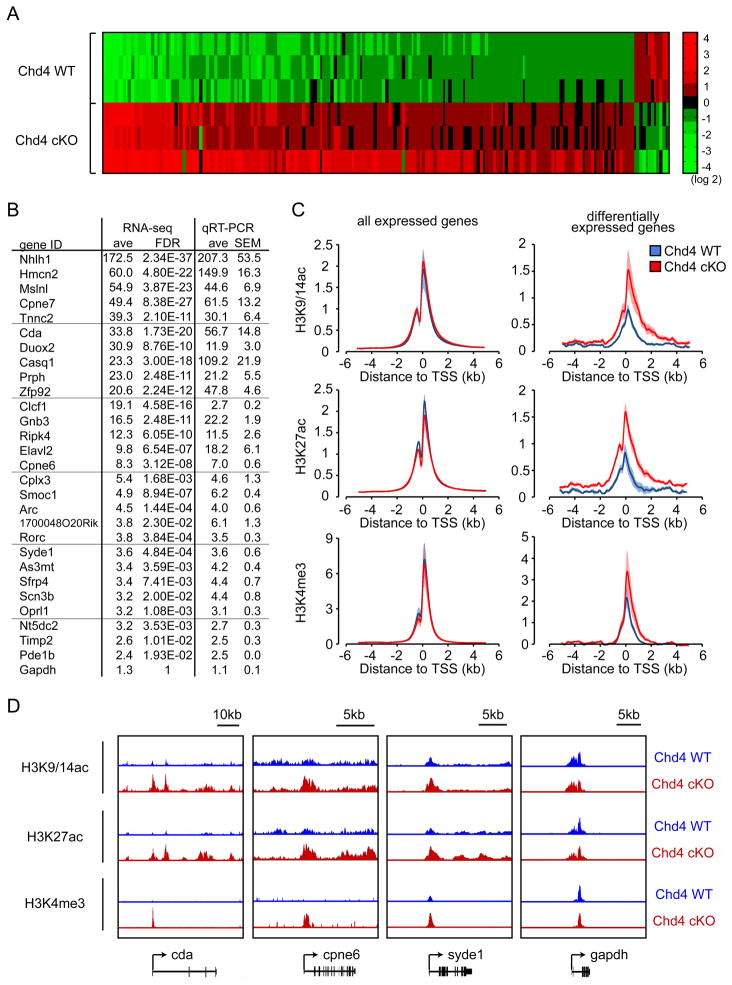
Figure 3. The NuRD complex decommissions the promoters of a specific set of genes and thereby represses their expression in the cerebellum in vivo.
(A) RNA was extracted from cerebella of P22 control Chd4loxP/loxP mice and Chd4 conditional knockout mice and subjected to RNA-Seq analyses. A heatmap of the expression levels of significantly differentially expressed genes between control Chd4loxP/loxP and Chd4 conditional knockout cerebella is shown (FDR<0.05, 3 independent brains per condition, base2 log-transformed mean centered). The vast majority (93%) of differentially expressed genes identified by RNA-Seq were derepressed in Chd4 conditional knockout cerebella. (B) RNA from P22 control Chd4loxP/loxP mice and Chd4 conditional knockout mice were subjected to qRT-PCR using primers specific to Chd4-regulated genes identified by RNA-Seq. Fold change of gene expression by RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR are shown. Changes in gene expression between Chd4loxP/loxP mice and Chd4 conditional knockout mice as measured by RNA-Seq are in good agreement with qRT-PCR analyses. The gapdh gene was included as a negative control. (C) Cerebella of P22 control Chd4loxP/loxP mice and Chd4 conditional knockout mice were subjected to ChIP-Seq analyses. The profiles of the transcriptionally-active histone marks H3K9/14ac, H3K27ac, and H3K4me3 surrounding the transcription start site (TSS) of all expressed genes (left panels) and NuRD-repressed target genes (right panels) are shown. The abundance of H3K9/14ac, H3K27ac, and H3K4me3 marks was increased at the promoters of NuRD-repressed target genes in Chd4 conditional knockout mice compared to control Chd4loxP/loxP mice. There were little or no differences in the genome-wide level of H3K9/14ac, H3K27ac, and H3K4me3 marks between Chd4 conditional knockout mice (Chd4 cKO) and control Chd4loxP/loxP mice (Chd4 WT). The shading denotes standard error. (D) Representative genomic regions of NuRD-regulated target genes are shown. The abundance of H3K9/14ac, H3K27ac, and H3K4me3 histone marks was increased at the promoters of the NuRD-targets cda, cpne6, and syde1, but not at the promoter of the control gene gapdh, in Chd4 conditional knockout mice.