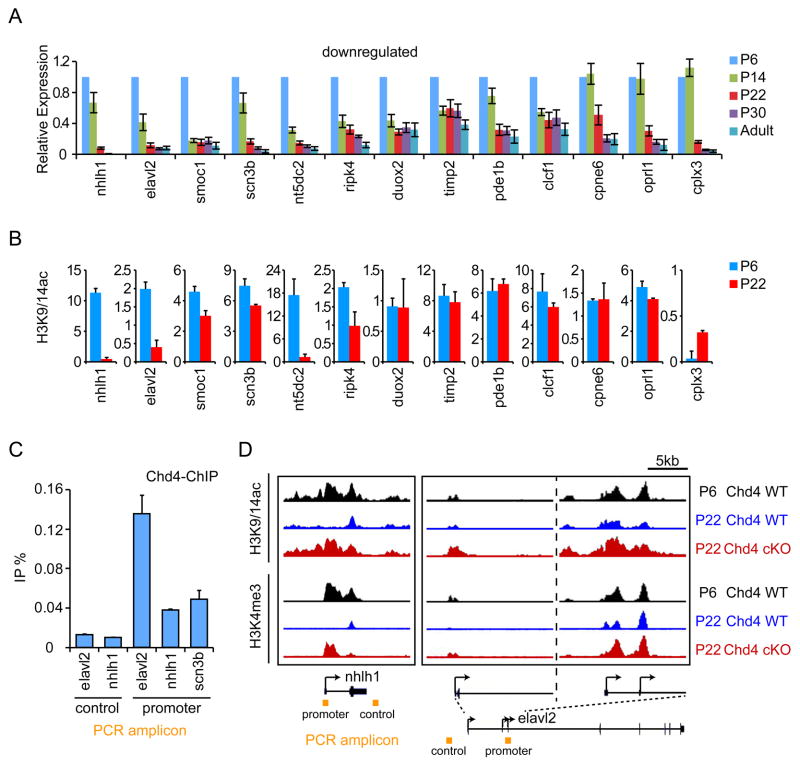
Figure 4. The NuRD complex orchestrates developmental repression of a program of genes that inhibit presynaptic differentiation in vivo.
(A) Total RNA of cerebella from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30, and during adulthood were subjected to qRT-PCR analyses using primers to a panel of NuRD-regulated genes. Gene expression was normalized to Gapdh expression. The majority of NuRD-regulated genes were progressively downregulated during cerebellar development. (B) Cerebella of P6 and P22 mice were subjected to ChIP-Seq analyses as in Figure 3C using the H3K9/14ac antibody. The sum of normalized H3K9/14ac reads in a 1 kb window centered at the +500 position relative to the TSS of NuRD-repressed target genes is shown. The abundance of histone H3K9/14ac is reduced at the promoters of the majority of developmentally downregulated NuRD target genes at P22 compared to P6. Error bars denote standard error of two biological ChIP-seq replicates. (C) P14 mice cerebella were subjected to ChIP-qPCR analyses using the Chd4 antibody and primers specific to the promoters of elavl2, nhlh1, and scn3b and control regions. Chd4 is enriched at target gene promoters (p<0.05, ANOVA followed by Fisher’s PLSD post hoc test, n=4). (D) Representative genomic regions of the nhlh1 and elavl2 genes in cerebella of control P6 and P22 Chd4loxP/loxP mice (Chd4 WT) and P22 Chd4 conditional knockout mice (Chd4 cKO). The abundance of H3K9/14ac (top panels) and H3K4me3 (bottom panels) marks at the nhlh1 and elavl2 gene promoters was decreased at P22 (blue) relative to P6 (black) in the cerebellum in control Chd4loxP/loxP mice. By contrast, the abundance of H3K9/14ac (top panels) and H3K4me3 (bottom panels) marks in Chd4 conditional knockout mice at P22 (red) was similar to that in control Chd4loxP/loxP mice at P6 (black).