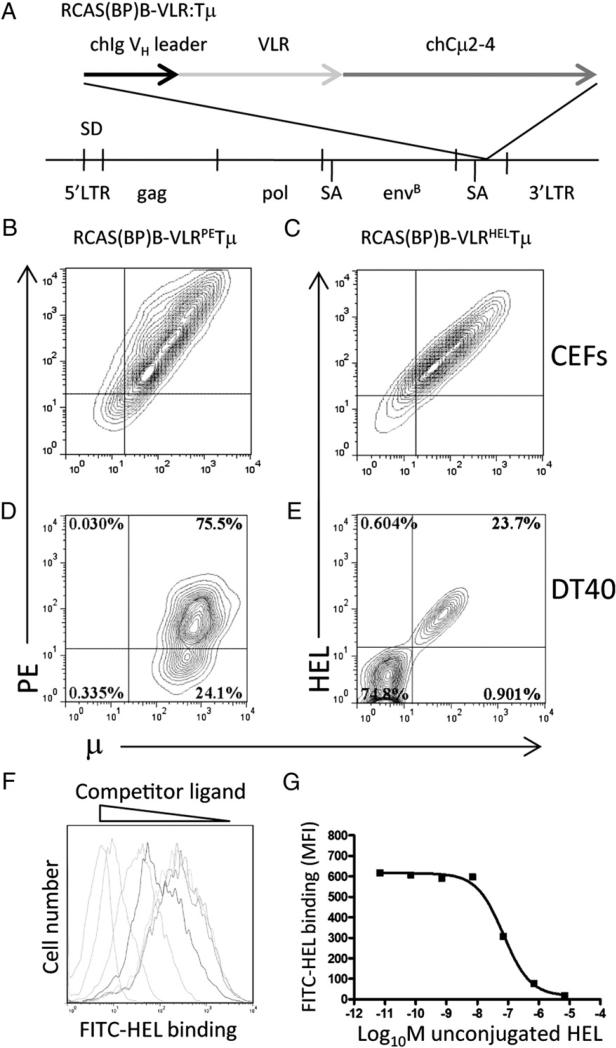
FIGURE 1.
VLRPETμ and VLRHELTμ receptor expression in chicken cells. (A) Schematic structure of RCAS(BP)B–VLRHEL/PETμ. The VLR diversity region was fused between the chicken VH leader sequence and the truncated chicken (CH2–4) transmembrane m-chain. CEFs were transfected with RCAS(BP)B–VLRPETμ (B) or RCAS(BP)B–VLRHELTμ (C), and surface expression and specificity of the chimeric receptors were assessed. Contour plots are gated on forward scatter and side scatter and are representative of 10,000 cells stained with anti-μ and specific Ag. sIg− DT40 chicken B cells were infected with RCAS(BP)B–VLRPETμ (D) or RCAS(BP)B– VLRHELTμ (E); VLR expression and Ag binding were assessed by anti-μ and specific Ag staining. Contour plots are gated on forward scatter and side scatter and are representative of 10,000 events. Binding affinity of the VLRHELTμ expressed on CEFs (F) was assessed by inhibition of binding by nonfluorescent HEL. Histograms are gated on forward scatter and side scatter and are representative of 10,000 events. (G) Affinity of binding was calculated by plotting the mean fluorescent intensity of bound fluorescent Ag versus concentration of competing nonconjugated HEL Ag.