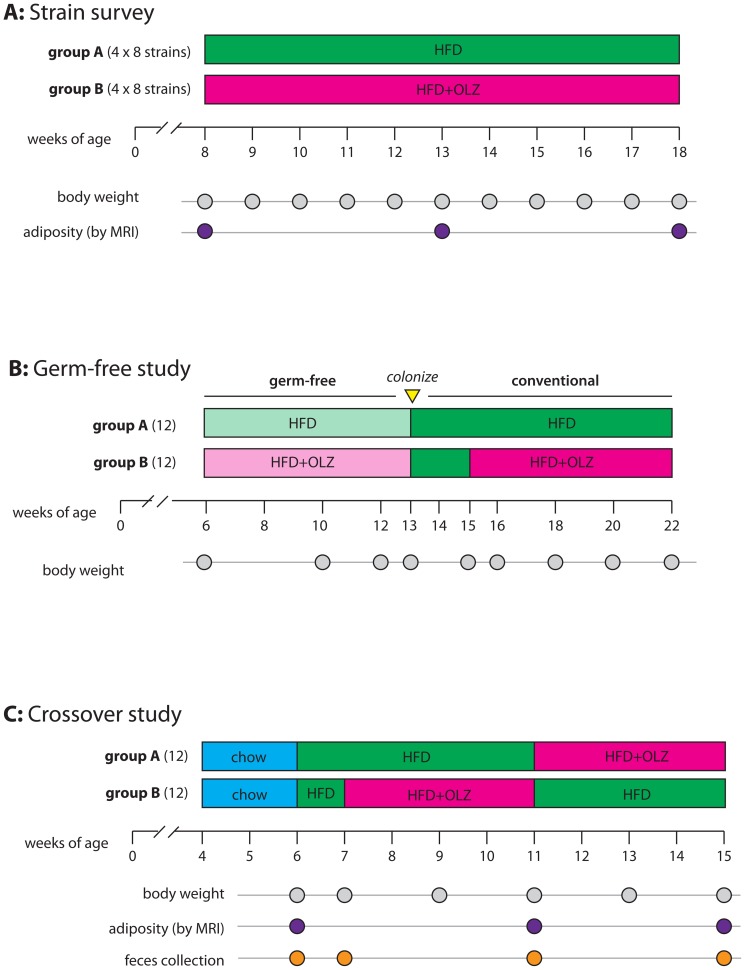
Figure 1. Experimental design.
(A) Eight groups of 8 female mice representing the founder strains of the Collaborative Cross project (A/J, C57BL/6J, 129S1SvlmJ, NOD/ShiLtJ, NZO/HlLtJ, CAST/EiJ, PWK/PhJ, WSB/EiJ) were received from the Jackson Laboratory at 6 weeks of age. Within each strain, mice were randomized to receive either olanzapine (OLZ, 50 mg/kg diet) or placebo while consuming a high-fat diet (HFD) ad libitum beginning at 8 weeks of age. Body weight was measured at time points indicated by grey dots; adiposity was measured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at time points indicated by purple dots. (B) Six cages of 4 female C57BL/6J mice were reared in germ-free (axenic) conditions. At 6 weeks of age, each cage was randomized to either HFD alone (3 cages; n = 12) or HFD plus OLZ (3 cages; n = 12). After 7 weeks of treatment mice were inoculated by oral gavage followed by a 2-week drug-free colonization period. Treatment was resumed for an additional 7 weeks under conventional housing conditions. (C) Two groups of 12 female C57BL/6J mice were received from the Jackson Laboratory at 4 weeks of age and randomized to study arms (group A or B). Both groups were acclimated to the facility for 2 weeks, during which time they were fed regular mouse chow, then both groups were switched to HFD for 1 week. For weeks 8–11, group A was maintained on high-fat diet and group B was switched to HFD plus OLZ. For weeks 12–15, groups were swapped so that group A received OLZ and group B received no drug. Body weight and adiposity phenotypes were collected at the indicated time points. Fecal pellets were collected for microbiome profiling at time points indicated by orange dots.