Fig. 1.
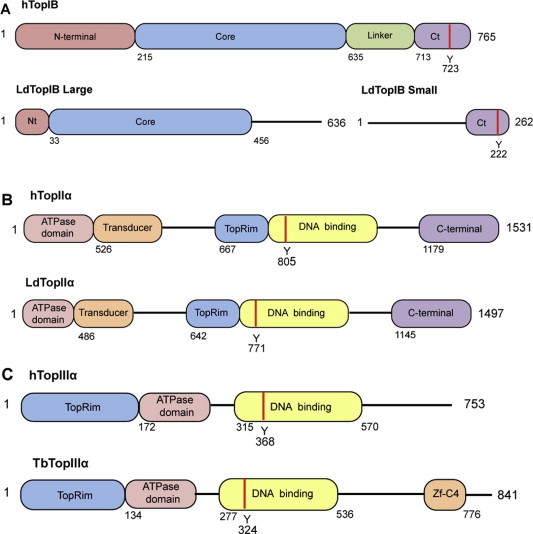
Schematic lineal representations of TopIB, TopII and TopIII from tritryps compared to human counterparts. (A) Human (top) and bisubunit L. donovani (down) TopIB, structural domains: Non-conserved hydrophilic N-terminal domain (Nt); central “core” domain with the representative active site amino acids (“tetrad”); non-conserved “linker” subdomain that connects “core” and the C-terminal domain and C-terminal domain (Ct) containing the DNA cleaving Tyr (red strip). (B) Human (top) and L. donovani TopII α (down) structural domains: N-terminal domain containing the ATPase and transducer domains; the Mg2+ binding site at the TopRim motif; a DNA binding that contains the DNA cleaving Tyr (red strip); C-terminal domain. (C) Human (top) and T. brucei TopIII α (down) structural domains: N-terminal domain containing the Mg2+ binding site at the TopRim motif; the ATPase domain and C-terminal domain; DNA binding site that contains the DNA cleaving Tyr (red strip); Znf-C4 (zinc-finger domain). Distances represented in the drawings are not in scale. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
