Figure 6.
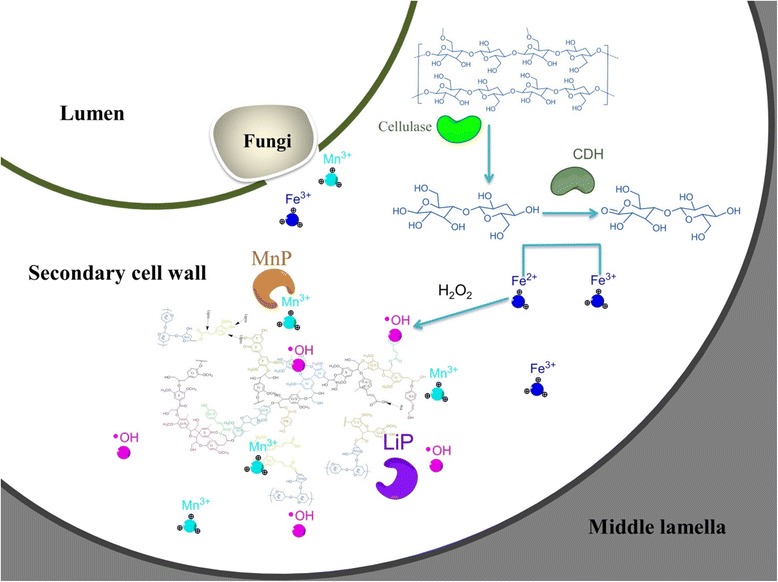
A proposed scheme of wheat straw cell wall degraded by Phanerochaete chrysosporium . Initial stage of the fungal growth is accompanied by hyphal attachment to the inner cell wall of the biomass. During growth, multiple enzymes are secreted, including cellulase, hemicellulase, and ligninase. Extracellular secretion of oxidases could participate in the generation of hydrogen peroxide and small carbon acids (such as acetate, succinate, and oxalate). Hydroxyl radicals, H2O2, and Fe3+ can be generated through synergistic interaction between cellobiose dehydrodrogenases (CDH), oxidases (copper radical oxidase among others), and the Fenton reaction. At the same time, Mn2+ is oxidized to Mn3+ by manganese peroxidase (MnP). The diffusion of these small radicals occurs predominantly in the secondary cell wall, which contains mainly the structural carbohydrates and aromatic backbone. The radicalization within the secondary cell wall contributes structural swelling by breaking the highly reactive ether linkages. This facilitates access of higher molecular weight enzymes.
