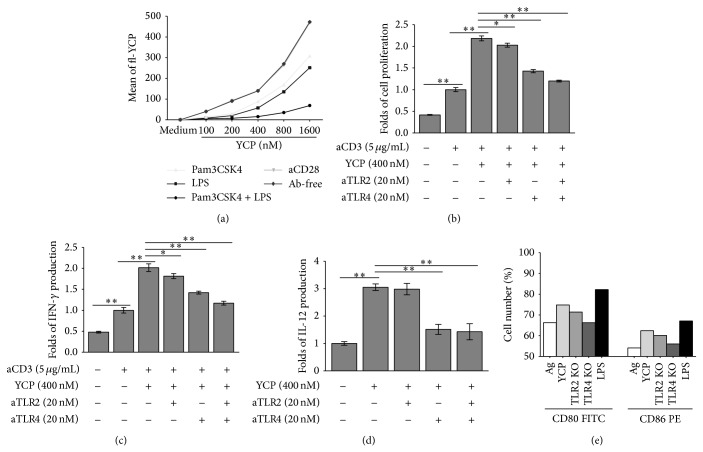
Figure 3.
The roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in the actions of YCP on T cells and DCs. (a) Ligand competition experiment on T cells. Splenic T cells were incubated with Pam3CSK4 (a bona fide TLR2 ligand), LPS (a bona fide TLR4 ligand), and anti-mouse CD28 (CD28 ligand) for 1 h, followed by fl-YCP (100–1600 nM) for 1 h in competition experiment analyzed by flow cytometry. ((b) and (c)) Splenic T cells prestimulated with aCD3 or PBS were pretreated with anti-TLR2, anti-TLR4, or both (20 nM) for 2 h before the addition of YCP. After 48 h incubation, cell proliferation (b) and IFN-γ concentration in supernatants (c) were measured using MTT assay or ELISA, respectively (n = 6, * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test). (d) DCs were pretreated with anti-TLR2, anti-TLR4, or both (20 nM) for 2 h before the addition of YCP. After 48 h incubation, IL-12 concentration in supernatants was measured by ELISA assay (n = 6, * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01 by Mann-Whitney U test). (e) The expressions of CD80 and CD86 treated by Ag (WT)/YCP+Ag (WT, TLR2 KO mice, TLR4 KO mice)/LPS (WT) were evaluated on DCs.