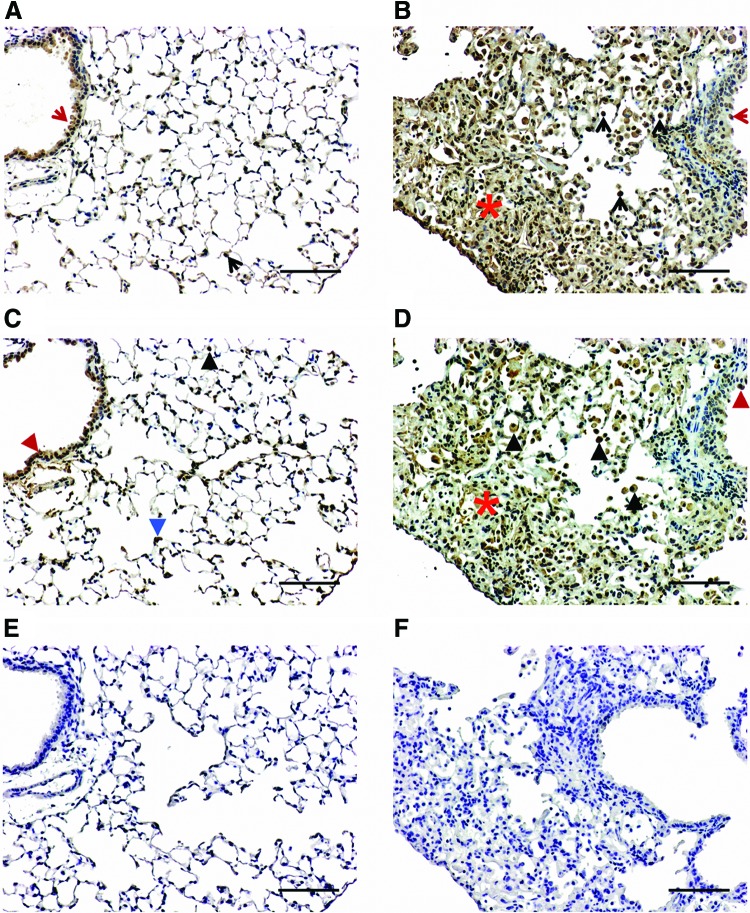
FIG. 7.
Immunoreactive VEGF-C and VEGF-D in control and radiated lungs. Representative images of VEGF-C (A and B) and VEGF-D (C and D) immunostaining visualized with diaminobenzidine (DAB) at 16 weeks post-irradiation. VEGF-C immunoreactivity was observed in epithelial cells (red arrow) and alveolar macrophages (black arrow) in both control (A) and radiated lungs (B). VEGF-D immunoreactivity was observed in epithelial cells (red arrowhead) and alveolar macrophages (recognized by their morphology and presence in the alveolar space; black arrowhead) in both control (C) and radiated lungs (D). Fibrotic areas in the radiated mouse lung (red asterisk) exhibited immunoreactivity for VEGF-C (B) and relatively weak immunoreactivity for VEGF-D (D), whereas VEGF-D was expressed within interstitial cells in control lungs (identified by their localization at the basal membrane side of alveolar epithelial cells, blue arrowhead, C). No staining was observed when primary antibodies were replaced with normal IgG (E and F). (Scale bar: 100 μm). A color version of this figure is available in the online article at www.liebertpub.com/lrb.