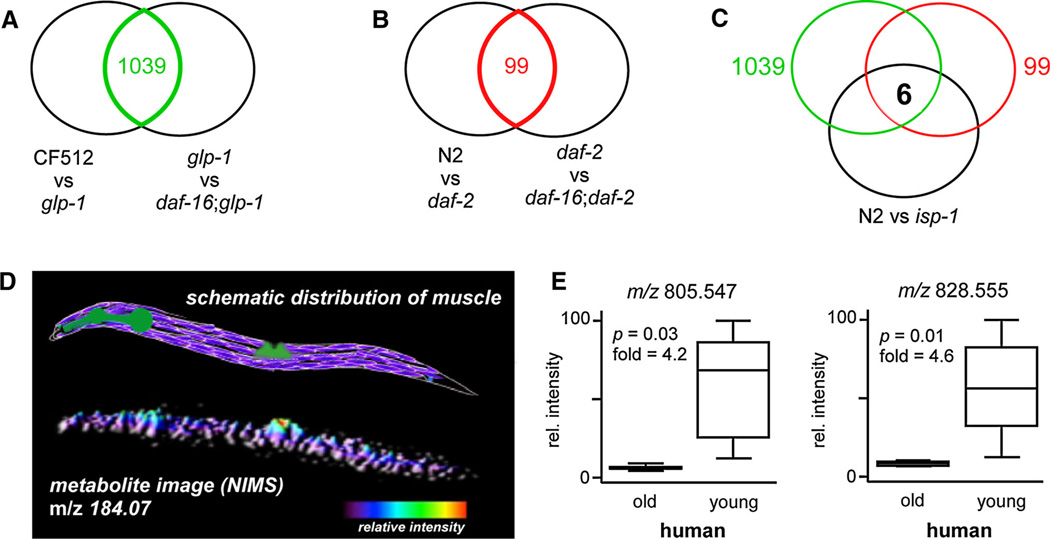
Fig. 1.
Metabolites associated with longevity revealed by metabolomics. a metaXCMS comparison of long-lived glp-1 to both its wild-type and a short-lived double mutant reveals shared metabolites that are uniquely altered in glp-1 induced longevity. b metaXCMS comparison of long-lived daf-2 to both its wild-type and a short-lived double mutant reveals shared metabolites that are uniquely altered in daf-2 induced longevity. c Three-way comparison of metabolites altered in long-lived glp-1, long-lived daf-2, and long-lived isp-1 relative to its wild-type identifies six shared alterations as potential age-related signaling molecules. Information about the chemical identities of these molecules is listed in Table 1. d Schematic distribution of muscle in C. elegans. Body-wall muscle is purple, pharyngeal and vulval muscle is green (top). NIMS image of characteristic fragment m/z 184.07 shows a strong localization of phosphatidylcholine to muscular region of worms (bottom). e Box plots of compounds that are down-regulated in elderly human quadricep muscle relative to young. These compounds are similarly altered in long-lived worms (Table 1)