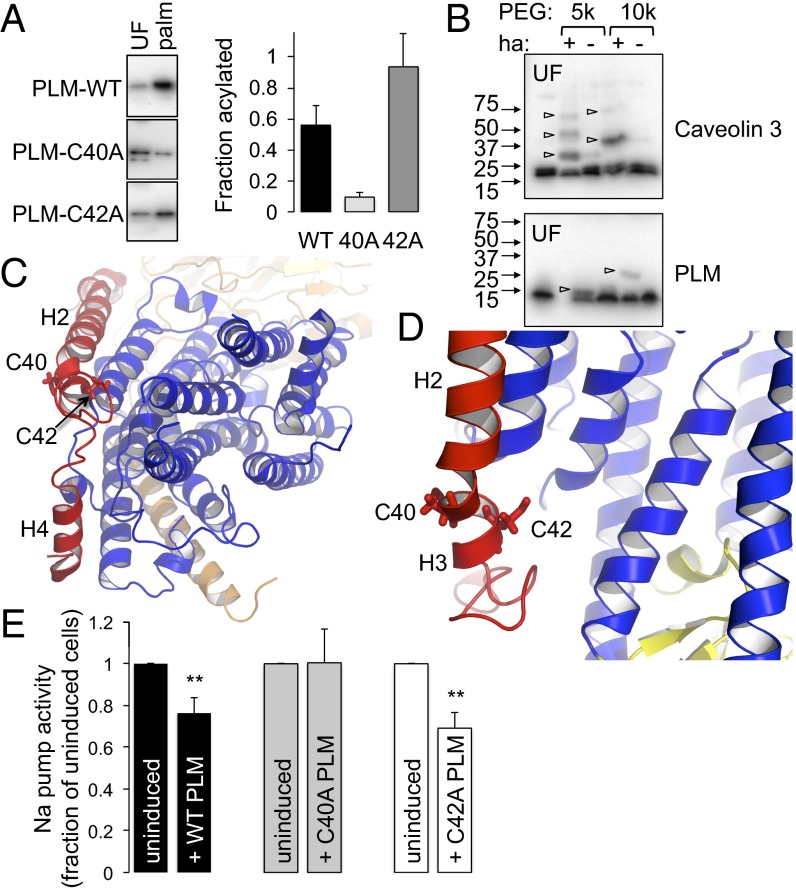
Fig. 4.
Analysis of PLM palmitoylation sites. (A) Palmitoylated proteins (palm) were purified by Acyl-RAC from FT-293 cells expressing wild-type, C40A, and C42A PLM. The relative enrichment compared with unfractionated cell lysates (UF) indicates PLM C40 is the principal palmitoylation site. (B) PEG switch assay from ventricular myocytes. Free cysteines were alkylated and lysates incubated in the presence of 5 kDa or 10 kDa PEG maleimide ± hydroxylamine (ha) to hydrolyze thioester bonds. PEGylation of previously palmitoylated cysteines retards mobility on SDS/PAGE. Caveolin 3 is triply palmitoylated and PLM singly palmitoylated in ventricular myocytes (arrowheads). (C) Position of PLM palmitoylation sites relative to the pump α-subunit. View is approximately perpendicular to the membrane from the cytoplasm. PLM is red, α-subunit transmembrane region is blue, and β-subunit is wheat. Helices H2, H3, and H4 of PLM are labeled. (D) C42 of PLM is orientated toward the α-subunit, and C40 away. The α-subunit P domain is yellow. (E) Na pump activity was measured as ouabain-sensitive 86Rb uptake by cells following induction of wild-type (WT), C40A, or C42A PLM–YFP. For simplicity, pump activity is expressed as a percentage of the activity in the same cells in which PLM expression was not induced. Wild-type and C42A PLM inhibit the Na pump, but C40A PLM does not (n = 7; **P < 0.01).