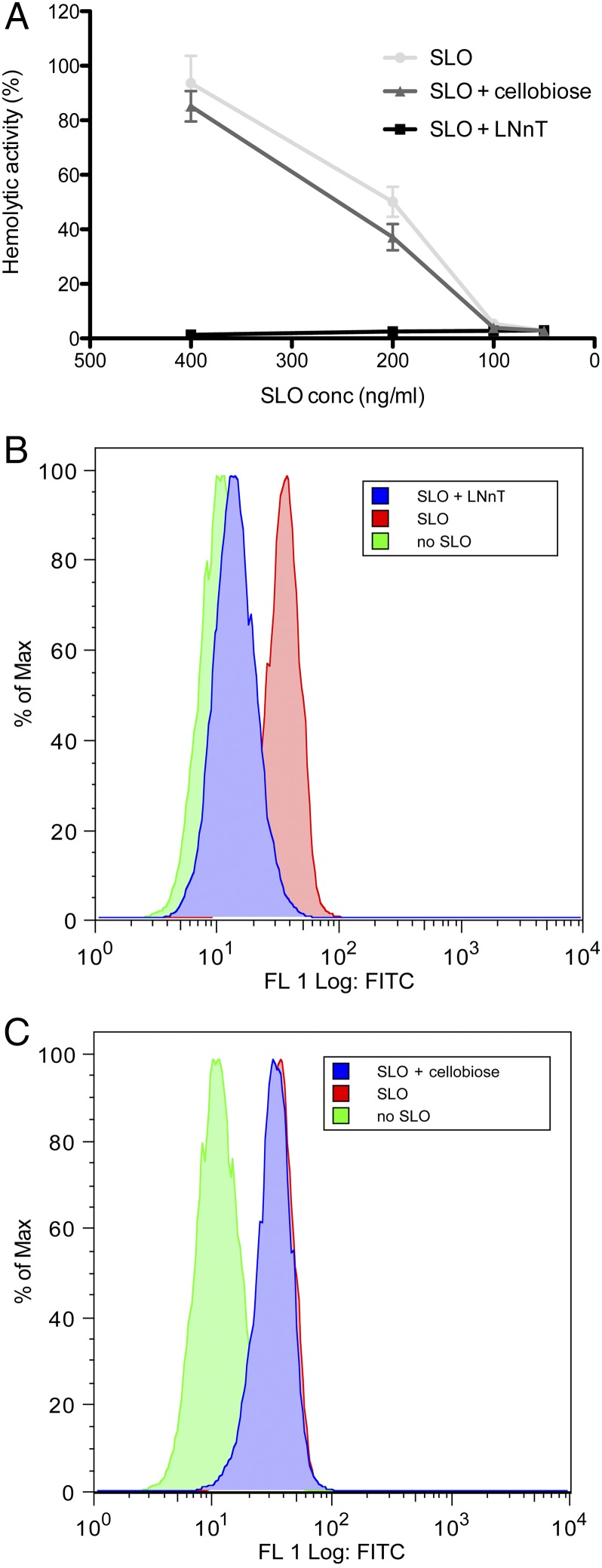
Fig. 8.
Phenotypic analysis of SLO function showing that hemolytic activity against human RBCs can be inhibited with LNnT by blocking binding of the toxin to the RBC membrane. (A) Hemolytic activity of a range of SLO concentrations (400 ng/mL, 200 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, and 50 ng/mL) against 1% (vol/vol) human group O RBCs at 37 °C for 30 min was determined after preincubation with PBS only (SLO), 2 mM LNnT, or 2 mM d-cellobiose. Results are presented as the mean of triplicate assays ± 1 SD. (B and C) Flow cytometric analysis of SLO binding to human RBCs. Human RBCs were incubated with 50 ng/mL SLO (SLO), 50 ng/mL SLO preincubated with 2 mM LNnT (SLO + LNnT), 50 ng/mL SLO preincubated with d-cellobiose (SLO + cellobiose), or PBS only (no SLO) on ice for 15 min. Binding of SLO to the RBC surface was detected with anti-SLO polyclonal mouse serum and preconjugated rabbit anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 and goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 antibodies.