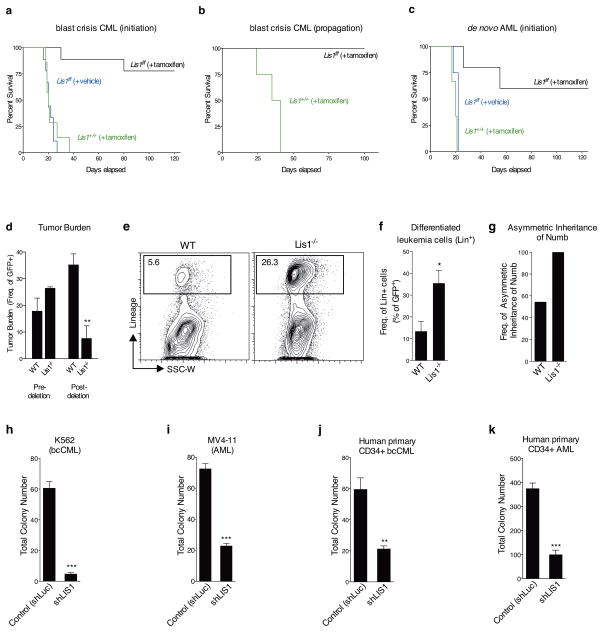
Figure 6. Loss of Lis1 impairs the development and propagation of myeloid leukemia in mouse models and human leukemia cells.
(a) Impact of loss of Lis1 on bcCML initiation. KLS cells from control (Lis1+/+; Rosa-creER) and Lis1f/f; Rosa-creER mice transduced with BCR-ABL-IRES-YFP and NUP98-HOXA9-IRES-GFP were transplanted into recipients, treated with tamoxifen and survival monitored. Data shown are from three independent experiments (n=9 for Lis1f/f +tamoxifen (black), n=9 for Lis1f/f +vehicle (blue) and n=7 for Lis1+/+ +tamoxifen (green)) (b) Impact of loss of Lis1 on propagation of established bcCML. Lin-negative cells from established control Lis1+/+creER or Lis1f/fcreER bcCML were transplanted into secondary recipients. Recipients were administered tamoxifen and survival monitored (n=4 for Lis1+/+, green and n=3 for Lis1f/f, black). (c) Impact of loss of Lis1 on de novo AML. KLS cells were isolated from control (Lis1+/+; Rosa-creER) and Lis1f/f; Rosa-creER mice and co-transduced with MLL-AF9-IRES-GFP and NRASG12V-IRES-YFP, treated with tamoxifen or corn oil and survival was monitored. Data shown are from two experiments (n=5 for Lis1f/f +tamoxifen (black), n=4 for Lis1f/f +vehicle (blue) and n=3 for Lis1+/+ +tamoxifen (green)). (d–f). Growth and cellular behavior of bcCML in vivo. Lineage-negative (Lin−) cells from control Lis1+/+; Rosa-creER or Lis1f/f; Rosa-creER established bcCML were transplanted into secondary recipients and (d) average tumor burden was tracked before (% of peripheral blood) and after (% of spleen cells) tamoxifen delivery; n=4 for control (WT) and n=3 for Lis1−/− mice; **P=0.0065. (e) Representative FACS plots show frequency of bcCML cells expressing lineage markers in control (WT) or Lis1−/− populations 1 day post-tamoxifen treatment. (f) Average frequency of bcCML cells expressing lineage markers (Lin+). Data shown are from two independent experiments (n=4 for WT and n=6 for Lis1−/−, *P=0.0282). (g) Frequency of leukemia cells undergoing asymmetric inheritance of Numb in control (WT) or Lis1−/− cells; n=22 cells for WT and n=7 cells for Lis1−/−. (h–k) Influence of Lis1 loss on human leukemia growth. Human leukemia cells were infected with either control (shLuc) or lentiviral shRNA targeting human LIS1 (shLIS1). Subsequently, infected cells were sorted and plated in methylcellulose. Colony formation was assessed in K562 blast crisis CML cells (h), MV4-11 AML cells (i), Imatinib, Nilotinib and Dastinib-resistant primary human CD34+ bcCML (j) and primary human CD34+ AML (k); One patient sample was tested for each leukemia with n=3 technical replicates, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).