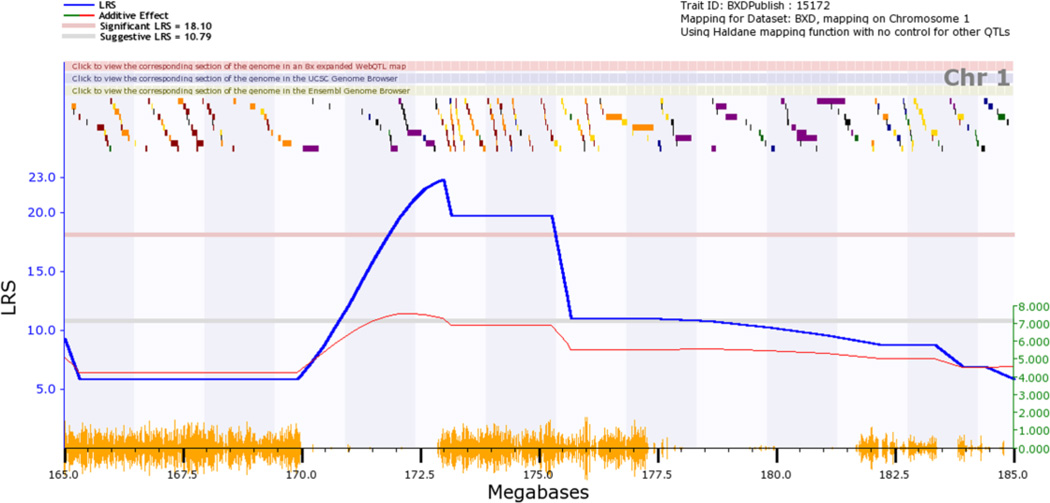
Figure 5.
Map of the genetic location on Chr 1 that modulates performance on the water maze task. This is a zoomed version of Fig. 4 that can be generated by clicking on the number at the top of the graph to get a Chr 1-specific QTL map and then by clicking on the red track at the top of the Chr 1 map to zoom in on the targeted Mb region. The locations of individual genes (colored blocks along the top) are superimposed above the LRS score in blue. The thin red line indicates the average effect of switching out a D allele for a B allele. In this case, this so-called additive effect increase the time spent searching for the platform by about 7 seconds per allele (right y-axis). The orange hash on the x-axis highlights the numerical density of sequence differences between the two parental strains. Two large regions are highly diverse and two large regions are very similar between parents.