Figure 3.
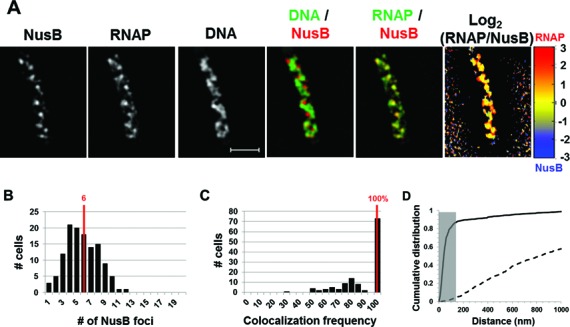
Nascent rRNA-binding protein NusB forms foci and co-localizes with transcription foci in fast-growing cells. (A) Images of NusB, RNAP, DNA (nucleoid), overlays of NusB (red) and DNA (green), RNAP (green) and NusB (red) and log2 (RNAP/NusB) (heat map) from a representative fast-growing E. coli cell as described in the legend to Figure 1. Similar to NusA, NusB foci are at the periphery of the nucleoid and that NusB signals perfectly co-localize with RNAP signals (overall yellow color on the RNAP/NusB overlay and on the heat map). (B) The distribution of apparent NusB-mCherry foci in fast-growing cells. The red line in the histogram indicates the median number of NusB foci in the population of cells. Note that the median number of NusB foci is close to that of NusA or transcription foci in fast-growing cells. (C) Co-localization frequency between the NusB foci and transcription foci in fast-growing cells. The red line indicates the median co-localization frequency of NusB foci with transcription foci in the population of cells as described in the Materials and Methods section. Almost all of the NusB-mCherry foci co-localize with at least one transcription foci in the cells. The average co-localization frequency of NusB foci and RNAP foci from a random data set is 0%. (D) Cumulative distribution of the distances between NusB foci and their closest RNAP foci in the population of cells as described in the Materials and Methods section. (──) NusB-mCherry RNAP-Venus and (- - -) NusB-mCherry RNAP-Venus random. The gray rectangle represents the co-localization area (≤140 nm). 87.1% of the NusB foci are within 140 nm of the closest transcription foci.
