Figure 5.
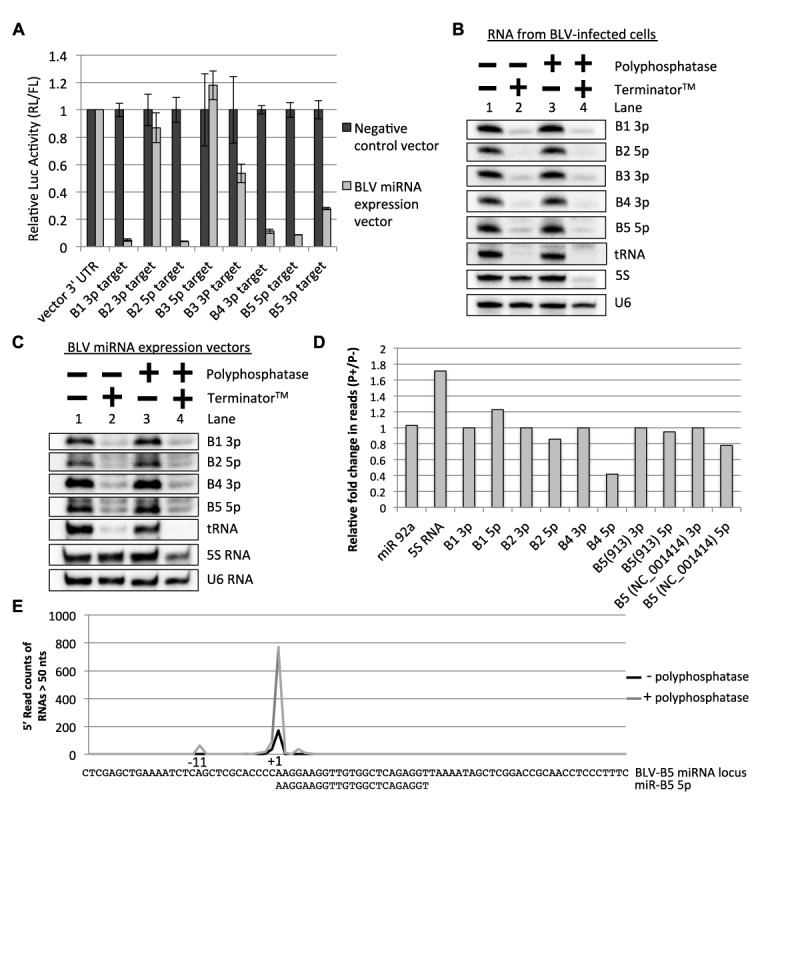
BLV 5p miRNAs contain a 5′-monophosphate. (A) RISC reporter assay. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with either irrelevant miRNA expression vector or an individual BLV miRNA expression vector and the respective Rluc vector encoding two complementary target sites to the indicated miRNAs. The graph depicts the average luciferase activity ratio (Ren/FF) +/− standard deviation (n = 3) normalized to vector 3′ UTR. (B) 5′-end characterization of BLV miRNAs from BLV-infected cells. Small RNAs were isolated from BL3.1 cells, treated with the indicated enzymes and northern blot analysis was performed. (C) 5′-end characterization of BLV miRNAs. Northern blot analysis was performed on small RNAs purified from HEK293T cells transfected with BLV miRNA expression vectors and treated with the indicated enzymes. (D) Graph representation of the fold change in the number of small RNA-seq reads, relative to the respective predominant 3p miRNA isoform, for each predominant BLV 5p miRNA isoform with or without RNA 5′ polyphosphatase pre-treatment. (E) Graphical representation of the 5′-read counts of pre-miRNA-sized RNAs (>50 nt in length) that map to the BLV (NC_001414) B5 miRNA locus (30 nt upstream and 54 nt downstream of the 5′-end of the predominant BLV-miR-B5 5p isoform) with and without RNA 5′ polyphosphatase pre-treatment. The number of reads of the pre-miRNA-sized RNAs was normalized to the predominant BLV-miR-B5 3p miRNA isoform in each dataset (Supplementary Table S2). The nucleotide positions are relative to the 5′-end of the predominant BLV-B5 5p miRNA isoform (+1).
