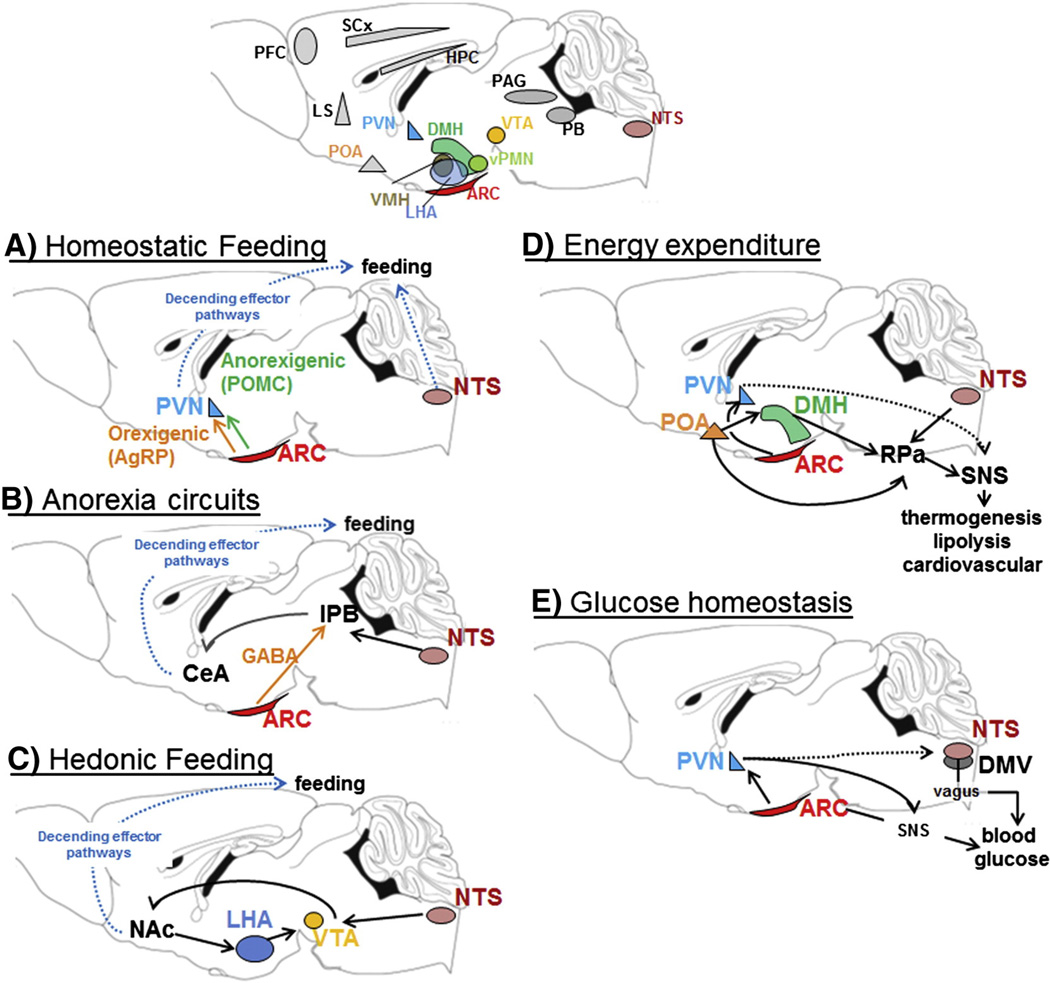
Fig. 3.
Central LepRb expression sites and related neuronal circuits. Leptin acts on diverse central circuits to regulate distinct aspects of energy homeostasis. A–E: Examples of select central circuits that have been studied in more detail for leptin function. Many other LepRb populations (gray areas in top panel) remain to be studied and integrated into a comprehensive picture of energy homeostasis. Specifically higher, cortical brain structures and descending effector pathway have not been well integrated into leptin regulated energy homeostasis. PVN = paraventricular nucleus; ARC = arcuate nucleus; NTS = nucleus of the solitary tract; AgRP = agouti-related-peptide; POMC = proopiomelanocoritin; CeA = amygdala; lPB = lateral parabrachial nucleus; GABA = γ-aminobutyric acid; Glu = glutamate; Nac = nucleus accumbens; LHA = lateral hypothalamic area; VTA = ventral tegmental area; POA = prooptic area; DMH = dorso-medial hypothalamus; RPa = raphe pallidus; SNS = sympathetic nervous system, DMV = dorso-motor complex of vagus; PAG = periaqueductal gray; SCs = sensory cortex; HPC = hippocampus.