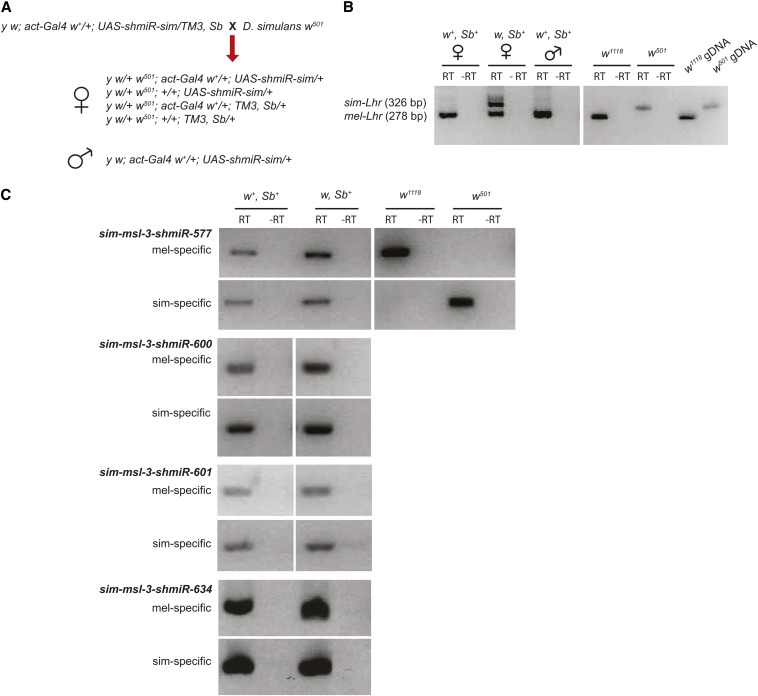
Figure 4.
RT-PCR tests of shmiR knock-down of D. simulans Lhr and msl-3. (A) D. melanogaster females expressing either Lhr or msl-3 siRNAs targeting the D. simulans orthologs (abbreviated as UAS-shmiR-sim) were crossed to D. simulans males. w+, Sb+ hybrid progeny (1/4 of the total) inherit both the Gal4 driver and UAS-shmiR. The males will survive if the UAS-shmiR construct knocks down expression of a hybrid lethality gene. (B and C) RT-PCR tests of knockdown. (B) Hybrid male and female progeny carrying both act-Gal4 and UAS-shmiR-sim-Lhr (w+, Sb+) express D. melanogaster mel-Lhr (278 bp) but not sim-Lhr (326 bp), assayed using a single primer pair that detects an insertion in sim-Lhr. Hybrid females carrying only UAS-shmiR-sim-Lhr (w, Sb+) were used as a control and express both orthologs. Right panel is RT-PCR and genomic DNA (gDNA) controls from D. melanogaster w1118 and D. simulans w501. (C) None of four tested sim-msl3-shmiR constructs silence sim-msl-3 expression in hybrid female progeny. Separate PCRs were performed using primer pairs specific to either mel-msl-3 or sim-msl-3, as confirmed using controls as described previously. Hybrid females carrying both act-Gal4 and UAS-shmiR-sim-msl-3 (w+, Sb+) expressed both msl-3 orthologs. As a control, progeny only inheriting UAS-shmiR-sim-msl-3 (w, Sb+) were also assayed (except for sim-msl-3-shmiR-577 where both w, Sb+ and w, Sb animals were pooled), and expressed both orthologs as expected. RT-PCR, reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.