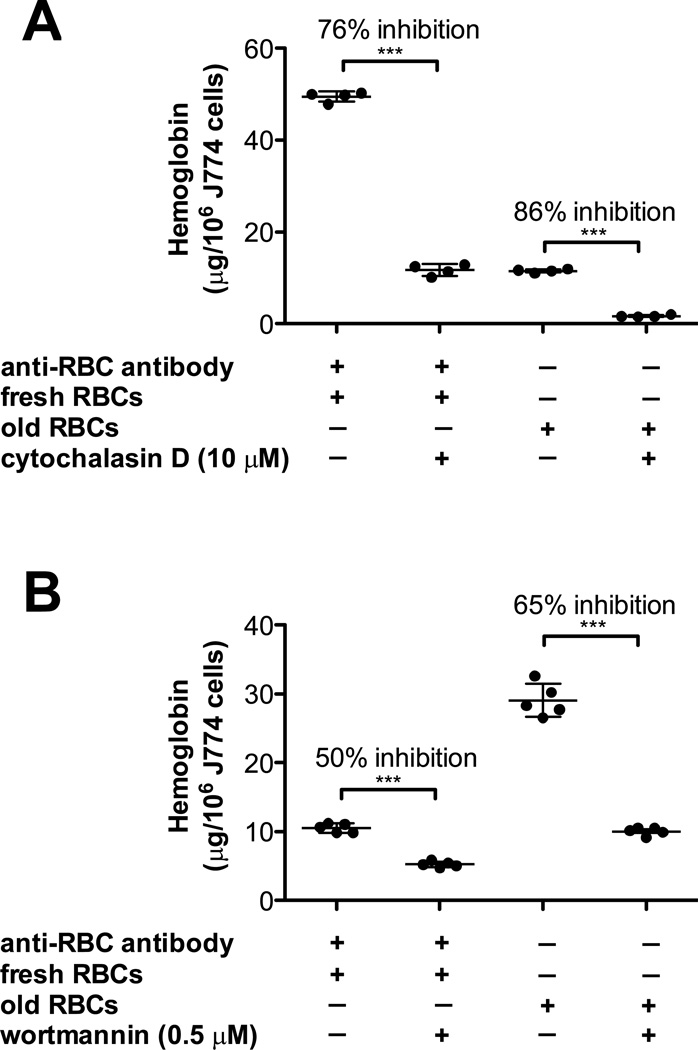
Figure 2. The signal transduction machinery required to ingest storage-damaged RBCs is similar to IgG-mediated phagocytosis.
(A) J774A.1 cells were incubated either with fresh RBCs in the presence of a sub-agglutinating concentration of rabbit IgG anti-mouse RBC antibody (left) or with 14-day refrigerator-stored RBCs (right) in the presence or absence of 10 µM cytochalasin D, an inhibitor of actin polymerization. The amounts of ingested RBCs were quantified by harvesting cells following osmotic shock, lysing the resulting J774A.1 cells, and measuring hemoglobin content. (B) J774A.1 cells were incubated either with fresh RBCs in the presence of a sub-agglutinating concentration of rabbit IgG anti-mouse RBC antibody (left) or with 14-day refrigerator-stored RBCs (right) in the presence or absence of 0.5 µM wortmannin, an inhibitor of phosphoinositide-3 kinase. The amounts of ingested RBCs were quantified, as described in Panel A.