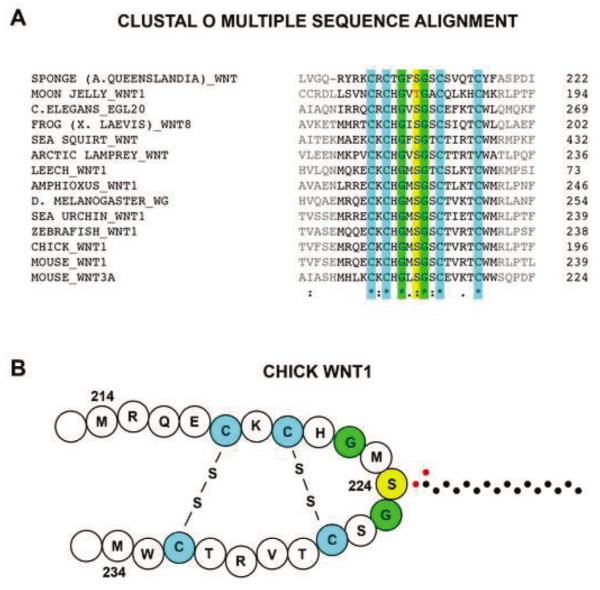
Figure 8. Cross-species alignment of Wnt1 shows a conserved serine or threonine residue involved in PORCN-dependent palmitoylation.
(A) A comparison of Wnt1 sequences of various animal species was performed using a Clustal Omega cross-species alignment. The sequences corresponding to the 31-residue fragment are shown in this alignment. The 5 amino acids on each end of this peptide, which are not required for palmitoylation, are shown in gray. This alignment shows that the moon jelly has a threonine residue in place of the serine. Furthermore, the conservation of only 6 of the 20 internal residues flanking the palmitoylated serine/threonine (yellow) suggest the importance of the four cysteine residues (green) and the two glycine residues (blue). (B) Based on the known structure of XWNT8 [30], we present a working model of the secondary structure of chick WNT1. The carbons of the palmitate group are shown as black dots while the oxygens are depicted by red dots. Symbols are defined as follows: “*” = identical; “:” = conserved substitution; “.” = semi-conserved substitution.