Figure 3.
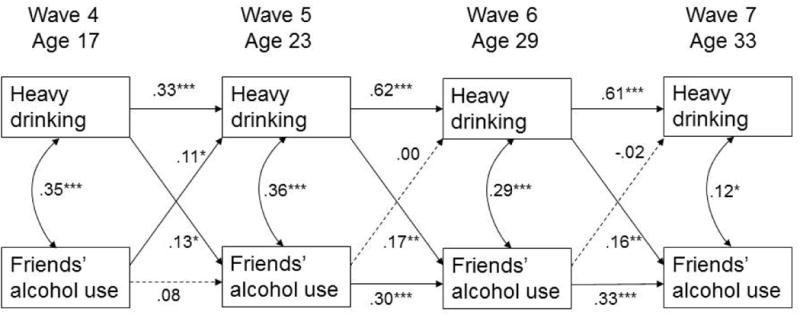
Autoregressive cross-lagged model of reciprocal relationships between heavy drinking and friends' alcohol use.
Note: Coefficients are standardized. Dashed lines are not significant. All paths are adjusted for sex, racial/ethnic minority status, and current age, family income, and marital status. Heavy drinking is measured as the long-transformed average number of days per month when the participant consumed 6 or more alcoholic drinks in a row in the last 6 months; friends' alcohol use is assessed as a percentage of close friends drinking alcoholic beverages at Wave 4 and as a percentage of close friends considered to be heavy drinkers at Waves 5-7.
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001.
