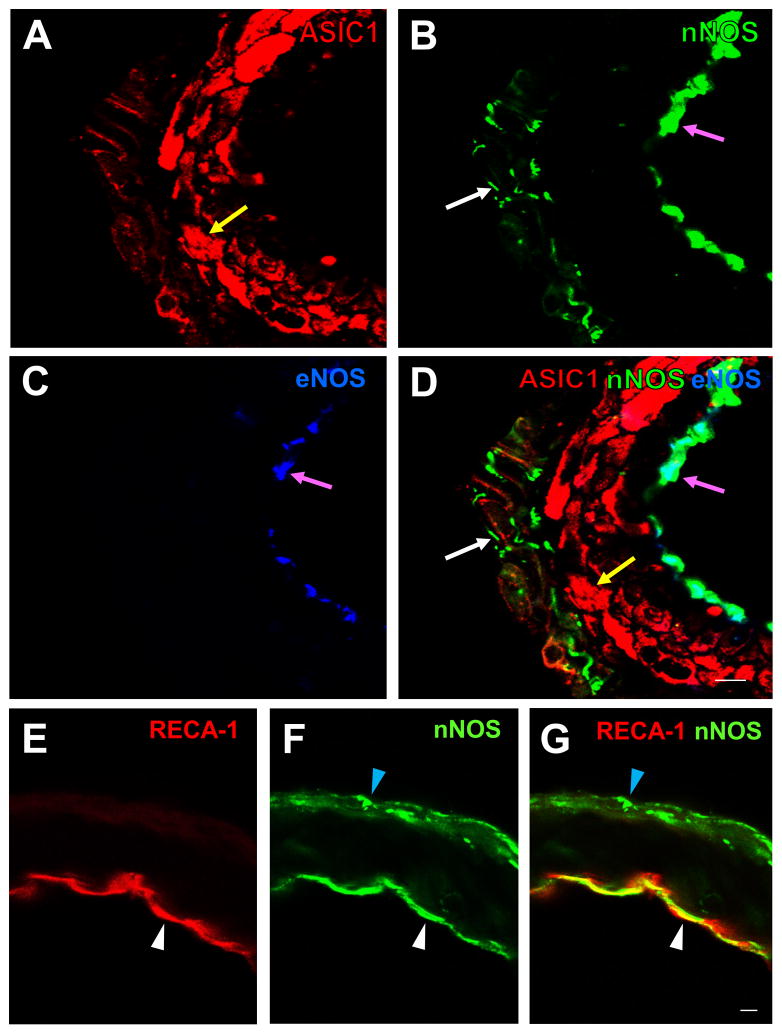
Fig. 4.
(A–D): High magnification confocal images of rat ACA showing triple-labeling fluorescent immunostaining for ASIC1 (A, red, RRX), nNOS (B, green, DyLight 488), and eNOS (C, blue, DyLight 649). ASIC1-IR (yellow arrow in A and D) is present in the smooth muscle layer, nNOS-IR in the adventitial layer (white arrows in B and D) and the endothelial layer (pink arrows in B and D), and eNOS-IR in the endothelial layer (pink arrows in C and D). Similar localization of ASIC1-IR, nNOS-IR and eNOS was also seen in the MCA, PCA and BA (not shown). A merged image (D) shows that nNOS-IR colocalizes with eNOS-IR in the endothelial layer (pink arrows in B, C and D) but not in the adventitial layer. (E–G): Confocal images of rat ACA showing double-labeling fluorescent immunostaining for the endothelial cell marker RECA-1 (E, red, RRX) and nNOS (F, green, DyLight 488). A merged image (G) shows that nNOS-IR colocalizes with IR of RECA-1 in the endothelial layer (white arrow heads in E–G), but not in the adventitial layer where RECA-1 was not found (blue arrow heads in F and G). Scale bar = 10 μm.