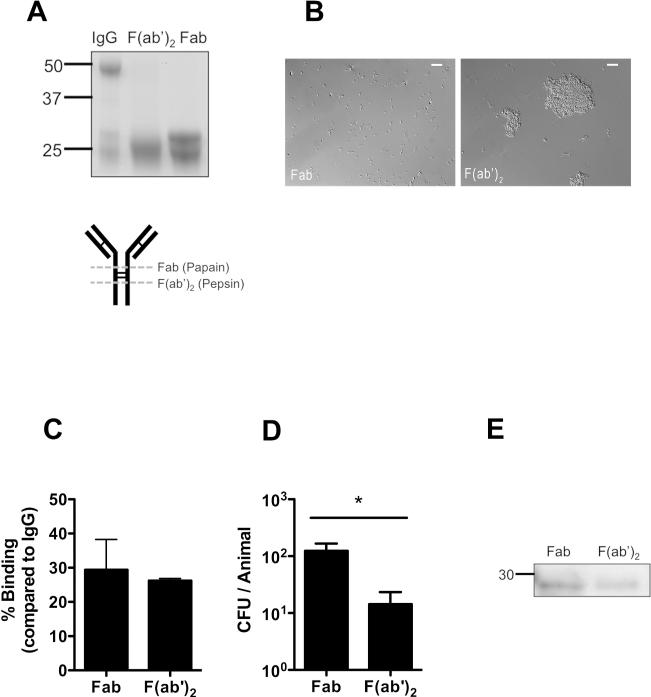
Figure 7. Agglutination enhances protection by antibody.
TS IgG was cleaved into either F(ab’)2 or Fab fragments by pepsin or papain, respectively. (A) IgG, Fab and F(ab’)2 fragments were separated on a reducing SDS-PAGE gel and detected by coomassie to determine the completeness of digestion. Size markers in kilodaltons. Schematic of IgG digestion is shown, with dashed line indicating enzymatic cleavage sites relative to disulphide bonds (thin lines). (B) S. pneumoniae was incubated with Fab or F(ab’)2 fragments and agglutination was visualized by Nomarski microscopy with 200x magnification, with 20micron scale bars. (C) Binding of Fab and F(ab’)2 fragments to immobilized capsular polysaccharide was quantified by ELISA, and shown as the % binding compared to whole IgG ± SEM. (D) Mice were passively immunized with equivalent concentrations of IgG fragments and challenged with 104 pneumococci (type 14) 4 hours later. CFU/animal was determined 24 hours post immunization ± SEM. n≥ 12 mice per group. * P<0.05. (E) Western blot analysis of nasal lavages from mice immunized 4 hrs prior with either Fab or F(ab’)2. Antibody fragments were detected with anti-rabbit IgG (F(ab’)2 specific) using horseradish peroxidase under reducing conditions. Size marker in kilodaltons.