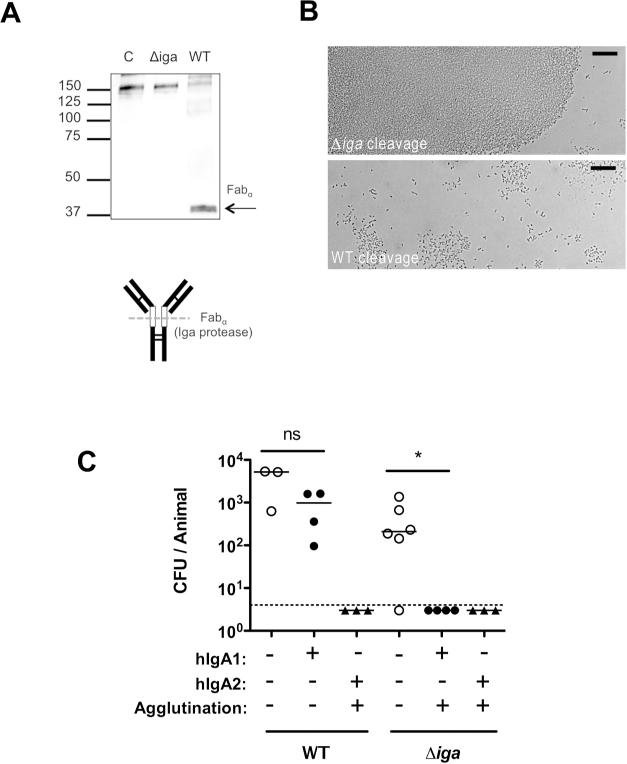
Figure 9. Bacterial IgA1 protease eliminates mucosal protection by human IgA1.
(A) Human monoclonal IgA1 was incubated overnight with wild-type (WT) or IgA1 protease deficient (Δiga) pneumococci (type 2). The supernatant was analyzed by Western blot detecting hIgA1 by anti-human IgA antibody (α-chain specific) using alkaline phosphatase under non-reducing conditions. Size markers in kilodaltons. Schematic of IgA1 digestion to generate fabα is shown, with open boxes indicating the hinge region, and dashed line indicating protease cleavage site relative to disulphide bonds (thin lines). (B) S. pneumoniae was incubated with TS hIgA1 mAb following cleavage from WT or Δiga pneumococci, and agglutination was then visualized using Nomarski microscopy with 200× magnification, with 20micron scale bars. (C) Mice were passively immunized with 25μg/animal anti-type 2 hIgA1 or hIgA2 mAbs (or PBS vehicle control) and challenged 4 hours later with 103 WT or Δiga pneumocci (type 2). CFU/animal was determined 20 hours post challenge. The dashed line represents the limit of detection (4 CFU). n≥ 3 mice per group. ns, not significant. * P<0.05.