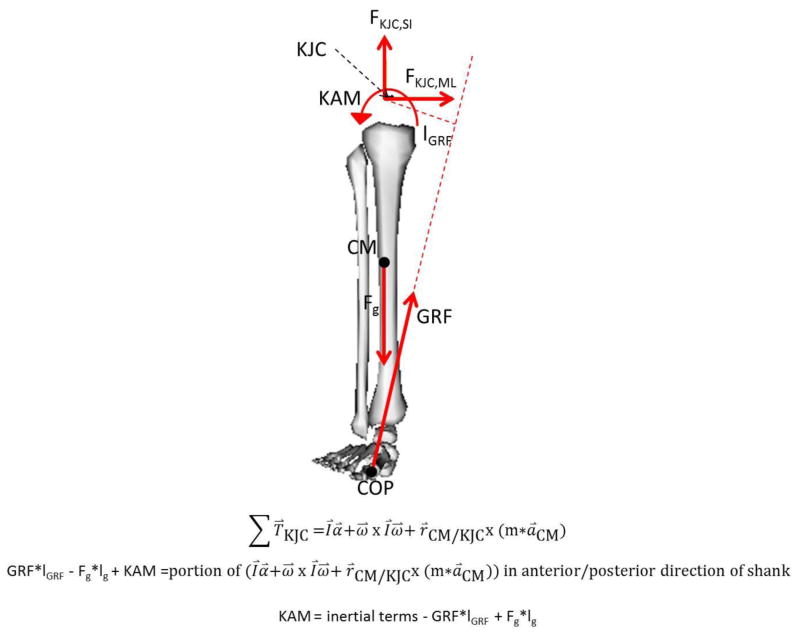
Figure 2.
Free body diagram of the lower limb with the equation (Newton’s equation of motion) used to calculate the knee adduction moment. TKJC = torque about the knee joint center (vector), I = inertia of lower limb (matrix), α = angular acceleration of lower limb (vector), ω = angular velocity of lower limb (vector), rCM/KJC = position vector from center of mass of the lower segment to the knee joint center, m = mass of lower limb (scalar), aCM = acceleration of lower limb (vector), GRF = magnitude of ground reaction force in frontal plane (scalar), lGRF = moment arm of frontal plane GRF (scalar), Fg = weight of lower limb (scalar), lg = moment arm of weight in frontal plane (scalar), KAM = knee adduction moment (scalar).