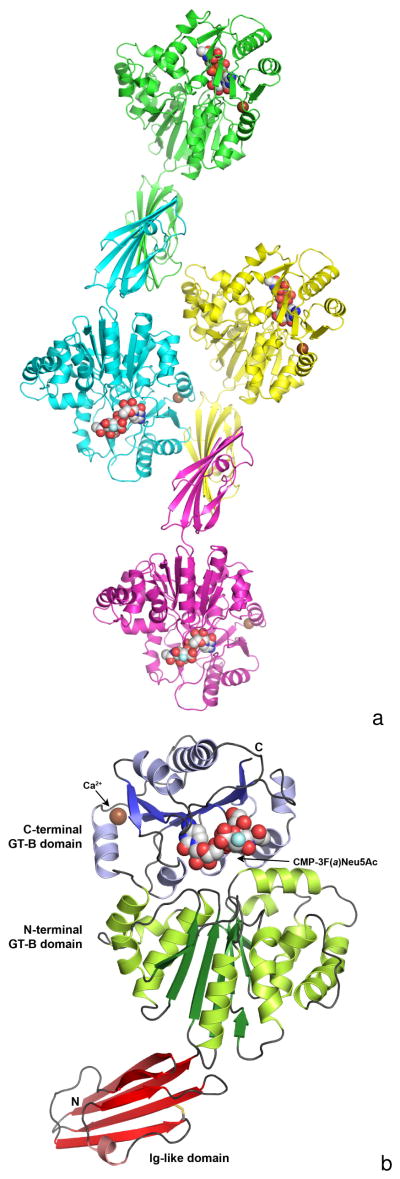
Figure 1.
Figure 1A. The composition of a crystallographic asymmetric unit. The structure of a Δ15Pd2,6ST(N) crystal soaked with CMP-3F(a)Neu5Ac is shown here in triclinic space group P1 with four monomers per asymmetric unit. Each monomer is colored differently, the calcium ions are illustrated as a brown-colored spheres and the bound CMP-3F(a)Neu5Ac molecules are shown as space filling spheres with white-colored carbon atoms. The fluorine atoms are colored light blue.
Figure 1B. A ribbon representation of the Δ15Pd2,6ST(N) monomer. The N-terminal Ig-like domain is at the bottom and is colored red, while the two-domain GT-B fold is at the top. The N-terminal GT-B domain is colored green (dark green for β-strands and light green for α-helices), while the C-terminal domain is colored blue (dark blue for β-strands and light blue for α-helices). The bound CMP-3F(a)Neu5Ac is represented by space filling spheres between the two Rossmann domains of the GT-B fold. The calcium ion is shown as a brown-colored sphere and the disulfide bond in the Ig-like domain is illustrated as sticks colored yellow.