Figure 1. Schematic of α-synemin and constructs used in in vitro assays.
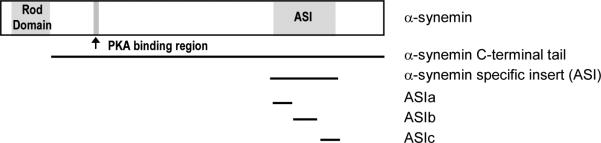
α-Synemin contains a very short head domain (10 amino acids), a rod domain (310 amino acids) allowing it to form heteropolymers with type III IF proteins, and a very long C-terminal tail classifying it as a type IV IF protein. It also contains a PKA RII binding domain classifying it as an AKAP. The 312 amino acid insert in the C-terminal tail (aa 1151-1462, ASI), absent in β-synemin, is the only difference between the two isoforms. For use in the yeast two-hybrid and GST pull down assays, the ASI peptide was subdivided into ASIa, (aa 1151-1243), ASIb (aa 1244-1358), and ASIc (aa 1359-1462).
