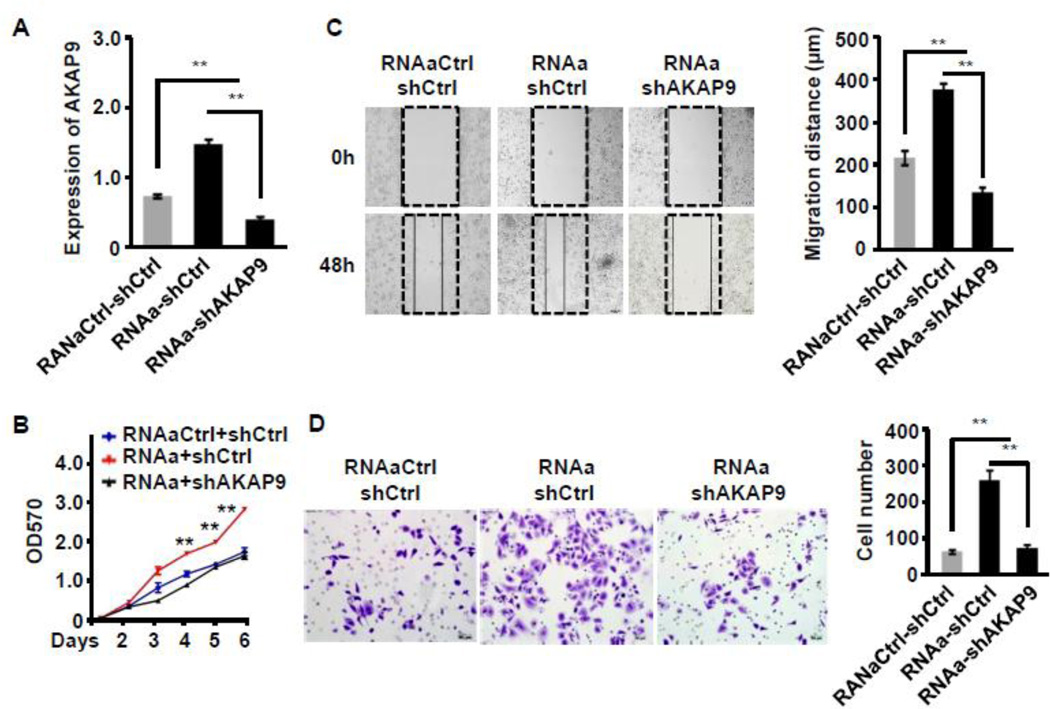
Figure 6. AKAP-9 was required for MALAT1-mediated CRC cell growth, migration and invasion.
SW480 cells were co-transfected control (RNAaCtrl) or MALAT1 saRNA (RNAa) with scramble (shCtrl) or AKAP-9 shRNA (shAKAP9) as indicated. Cell proliferation, migration and invasion were measured. (A) AKAP-9 expression was increased by RNAa activation but knocked down by shAKAP9. **P<0.01 (n=3). (B) Cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay. MALAT1 activation stimulated the SW480 cell proliferation, which was attenuated when AKAP-9 was knocked down. **P<0.01 compared to other two groups (n=3). (C) Cell migration was measured by wound-healing assay. Relative migration distance was 24 normalized to the original gap produced by inserts (0 h). **P<0.01 (n=3). (D) SW480 cell invasion was determined by matrigel invasion assay. MALAT1 induction enhanced SW480 cell invasion, which was attenuated by silencing of AKAP9. **P<0.01 (n=3).