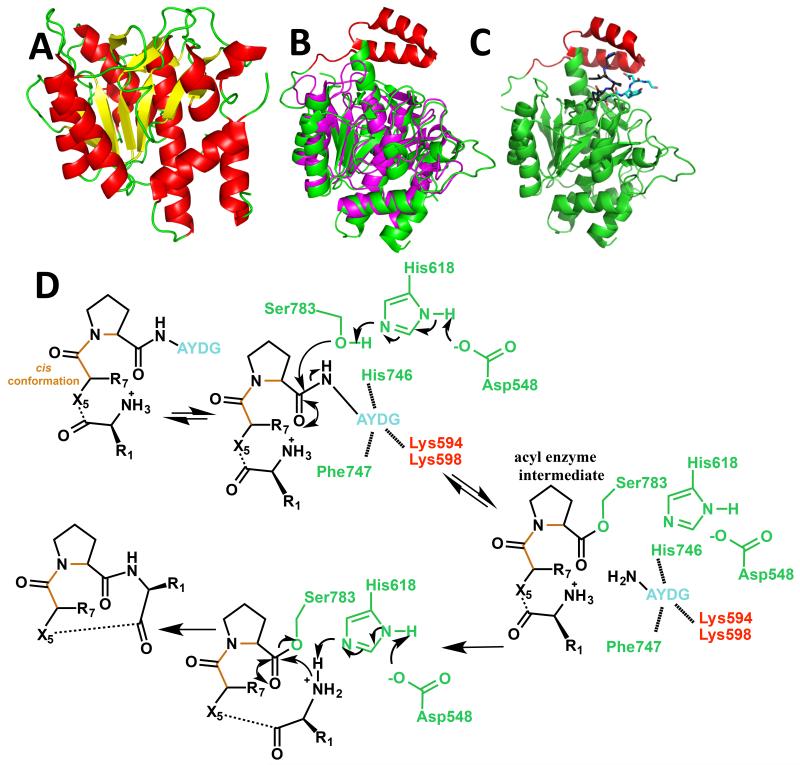
Figure 3.
(a) Crystal structure of the PatA protease domain [28• and 29••] in cartoon representation (colored as in Figure 2a);
(b) structural alignment of the PatG macrocyclase domain [30••] (subtilisin fold in green and ‘capping’ or ‘macrocyclization’ insert in red) with Akt1, a subtilisin protease (magenta);
(c) crystal structure of the PatG macrocyclase domain in complex with substrate peptide VPAPIPFPAYDG (only PIPFPAYDG ordered) [30••]. The cartoon of the protein is colored as 2b, the peptide is shown in stick with carbon atoms of the core peptide in black, carbon atoms of the macrocyclization signature in cyan, nitrogen atoms blue and oxygen atoms red; and
(d) mechanism for PatG macrocyclase domain catalyzed C-terminal cleavage of the core peptide to form an acyl enzyme intermediate and subsequent decomposition of this intermediate by the incoming amino terminus of the core peptide to form the macrocycle [30••]. The core peptide is shown in black, the macrocyclisation signature of the substrate is shown in magenta. The cis peptide is shown in orange. The protein residues are colored in green for those in the subtilisin fold and red for those in the insert.