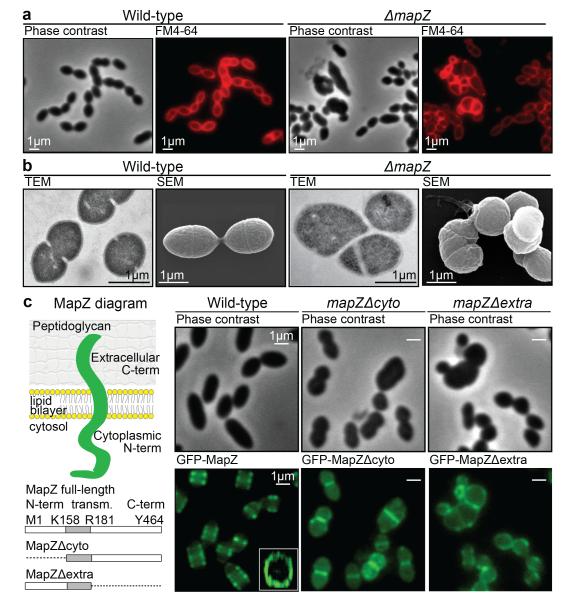
Figure 1. Characterization of MapZ.
a. Cell shape observed by phase contrast microscopy and after membranes staining with FM4-64. b. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). c. Diagram of MapZ domains prediction using TOPCONS (http://topcons.net, see methods), with an intracellular N-terminal domain, a transmembrane domain and an extracellular C-terminal domain. Wide-field microscopy images show the localization of GFP-MapZ full-length, GFP-MapZΔcyto and GFP-MapZΔextra deleted for the N-terminal or the C-terminal domain, respectively. Images are representative of experiments made in triplicate.