Abstract
Study Design:
Systematic review of the literature.
Objective:
To evaluate whether an integrated approach that includes different Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) therapies combined or CAM therapies combined with conventional medical care is more effective for the management of low back pain (LBP) than single modalities alone.
Summary of Background Data:
LBP is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, yet its optimal management is still unresolved.
Methods:
The PRISMA Statement guidelines were followed. The Cochrane Back Review Group scale was used to rate the quality of the studies found.
Results:
Twenty-one studies were found that met the inclusion criteria. The CAM modalities used in the studies included spinal manipulative therapy, acupuncture, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage therapy, and a topical ointment. Twenty studies included acupuncture and/or spinal manipulative therapy. Nine high quality studies showed that integrative care was clinically effective for the management of LBP. Spinal manipulative therapy combined with exercise therapy and acupuncture combined with conventional medical care or with exercise therapy appears to be promising approaches to the management of chronic cases of LBP.
Conclusions:
There is support in the literature for integrated CAM and conventional medical therapy for the management of chronic LBP. Further research into the integrated management of LBP is clearly needed to provide better guidance for patients and clinicians.
Key Words: Low back pain, complementary and alternative medicine, integrated care, acupuncture, spinal manipulation, systematic review
摘要
研究设计:系统性文献检查。
目的:评估包括不同的辅助和替 代医学(Complementary and Alternative Medicine, CAM)疗 法或CAM疗法结合常规医疗护理的 一种综合方法,是否比单一疗法 更有效的管理腰痛(Low back pain, LBP)。
背 景 资 料 概 述 : 在 世 界 范 围 内 , L B P 是 残 疾 的 主 要 原 因 之 一,但其最佳管理方法仍然没有 得到解决。
方法:遵照PRISMA声明的指南内 容 。 采 用 柯 克 兰 背 部 检 查 组 量 表,对研究质量进行评级。
结果:发现21项研究符合纳入标 准。研究中使用的CAM方法包括脊 椎手法治疗、针灸、运动疗法、 物 理 疗 法 、 按 摩 疗 法 和 外 用 药 膏。20项研究包括针灸和/或脊椎 手法治疗。9项高质量的研究表 明,综合护理是临床上有效的LBP 处理方法。结合传统的医疗或运 动疗法的脊椎手法治疗、以及结 合常规医疗或运动疗法的针灸方 法看来对于处理慢性LBP病例是有 前途的。
结论:文献支持综合性CAM与传统 医学可用于治疗慢性LBP。但是, 显然需要进一步研究LBP综合处理 方法,以便为患者和临床医生提 供更好的指导。
SINOPSIS
Diseño del estudio:
Revisión sistemática de la bibliografía.
Objetivo:
Evaluar si un enfoque integrado que incluya diferentes terapias de medicina alternativa y complementaria combinadas o las terapias de medicina alternativa y complementaria combinadas con cuidados médicos convencionales resulta más efectivo a la hora de controlar la lumbalgia que las modalidades individuales por sí solas.
Resumen de los antecedentes:
La lumbalgia es una de las principales causas de discapacidad en el mundo; sin embargo, aún se desconoce cómo tratarla de manera óptima.
Métodos:
Se siguieron las directrices de la Declaración PRISMA. Se empleó la escala del Grupo Cochrane de revisión de la espalda para calificar la calidad de los estudios encontrados.
Resultados:
Se encontraron 21 estudios que cumplían con los criterios de inclusión. Las modalidades de medicina alternativa y complementaria empleadas en los estudios incluían terapia de manipulación espinal, acupuntura, terapia basada en ejercicios, fisioterapia, terapia de masaje y pomada tópica. Veintiún estudios incluían acupuntura y terapia de manipulación espinal. Nueve estudios de alta calidad mostraron que la atención integral resultaba clínicamente eficaz para el tratamiento de la lumbalgia. La terapia de manipulación espinal combinada con el cuidado médico convencional o con la terapia de ejercicios y la acupuntura combinada con el cuidado médico convencional o con la terapia de ejercicios parecen constituir enfoques prometedores en el tratamiento de casos de lumbalgia crónica.
Conclusiones:
Existen teorías en la literatura médica que apoyan la integración de medicina alternativa y complementaria y la terapia médica convencional a la hora de tratar la lumbalgia crónica. Es necesaria investigación adicional para el tratamiento integrado de la lumbalgia que sirva de referencia a pacientes y médicos.
INTRODUCTION
Low-back pain (LBP) is a complex disorder and one of the most significant healthcare challenges affecting modern society. In the United States, LBP is the fifth most common reason for all physician visits1,2 and is the single most common cause for chronic or permanent impairment in adults under the age of 65 years.3 LBP is now considered the leading cause of disability worldwide.4 While substantial heterogeneity exists among epidemiological studies of LBP, estimates of the recurrence of activity limiting LBP at 1 year range from 24% to 80%,5 leading to a startling economic burden that appears to continue to increase.6
The number of interventions available to manage LBP is also extensive.7,8 While there are more than 1000 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published on the topic,9 the most effective management approach remains unclear.8,10 Conventional treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications have been shown to have limited benefit in improving patient outcomes.11 Opioids appear to offer short-term benefits for chronic LBP, but long-term effects and safety remain unproven.12 Stabilization exercises have been reported to help decrease pain and disability,13 and post-treatment exercise programs have been shown to prevent recurrences of back pain, but Choi et al.14 found conflicting evidence for exercise as a treatment. An RCT comparing fusion surgery with conservative treatment showed conflicting results as well.15 These uncertainties in the literature and in conventional medical practice may help explain why LBP is the most common reason for patients to seek out care from a complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) provider.16 Yet, the literature in support of CAM for management of LBP is also limited. A review published by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality found that CAM therapies for back pain (such as acupuncture, massage, and spinal manipulative therapy [SMT]) provide a greater, albeit a modest, benefit as compared to usual medical care.17
With so many treatment options available and insufficient evidence of efficacy,15 it is no surprise that there is little consensus among healthcare practitioners across disciplines and even within disciplines with regard to what might be the most appropriate management intervention for LBP. Hirsh et al18 reported that there does not seem to be a one-size-fits-all approach to LBP management, that no single treatment approach is the panacea for all patients.
Previous reviews2,19-28 have evaluated the use of single CAM therapies for LBP, but in practice it is also common for patients to seek care from multiple practitioners and therefore combine different types of therapies (such as combining conventional medical care, SMT, exercise, and/or acupuncture).8 National survey data suggest that more than half of US adults with LBP seek care from medical doctors and one or more types of CAM modalities.16 The increasing use and acceptance of CAM29 makes this combined approach to care likely to become even more prevalent in the coming years,30 yet very little information has been collected regarding the actual practice of integrative medicine for the treatment of LBP. Studies have proposed the use of multi-modal therapies for LBP management15 with Guzman et al31 reporting a benefit for multidisciplinary biopsychosocial rehabilitation for LBP and Flor et al32 finding multidisciplinary treatments for chronic LBP to be superior to single-discipline treatments such as medical treatment or physical therapy. However, Flor's32 review did not include RCTs, and neither Flor et al32 nor Guzman et al31 considered CAM therapies. Rubinstein et al27 included a review of SMT used as an adjunct therapy but limited their search to acute LBP and did not investigate any other CAM modalities. In Rubinstein's27 review of SMT for chronic LBP, SMT as an adjunct therapy demonstrated varying quality of evidence, but again, the study did not investigate other CAM modalities.20 No systematic reviews appear to have examined the studies that combine CAM modalities or CAM and conventional medical approaches for LBP. We therefore conducted a systematic review to address this gap in knowledge by summarizing efficacy evidence of an integrated approach to managing LBP.
Key Points:
Low back pain is a global disorder that causes significant disability.
People with low back pain often seek care from a variety of practitioners, both conventional medical practitioners and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) providers. The optimal management for low back pain is still debated.
This systematic review found 21 articles that described the management of low back pain by integrated therapy of conventional medicine and CAM modalities or CAM modalities combined.
Spinal manipulative therapy combined with conventional medical care or with exercise therapy and acupuncture combined with conventional medical care or with exercise therapy appear to be promising approaches to the management of chronic cases of low back pain.
Our aim was to summarize evidence in relation to the following questions:
Is an integrated approach that includes CAM therapies and conventional medical care more effective for the management of LBP than either alone?
Is an integrated approach that combines CAM modalities more effective than each applied alone?
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews was used as guide during the development of this project.33
Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible for this systematic review, articles had to meet the following criteria:
Reported on an RCT.
Included the treatment of LBP.
At least one treatment group received integrated therapy that included at least one CAM modality (ie, two or more CAM modalities used together, or one or more CAM modalities used with conventional medical treatment). For this study, a CAM modality was defined as a non-mainstream health-care intervention that is used either together with conventional medical care or in place of it.34 Conventional medicine was defined as care provided by a medical or osteopathic physician or allied healthcare providers (eg, physical therapist). Exercise therapy was defined as conventional medical care as it is most often considered a mainstream therapy provided by physical therapists.
Published in English.
An original study and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
At least one outcome measure for pain or disability used (visual analog scale for pain [VAS], Oswestry Low Back Pain Disability Questionnaire [Oswestry], Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire [Roland-Morris], Short Form-36 [SF-36], von Korff Scales, Dartmouth-Northern New England Primary Care Cooperative Information Project [CO-OP], Aberdeen Low Back Pain Scale (Aberdeen), McGill Pain Questionnaire [MPQ], Numeric Rating Scale for Pain [NRS], Rating of Perceived Capacity of Spine, self-generated pain or disability questionnaires).
Information Sources
The search engines used for this systematic review were PubMed, Medline, Index to Chiropractic Literature, Academic Search Premier, CINAHL, Cochrane Center Registry of Controlled Trials, and OVID. References of selected articles were searched for any additional studies that were missed by the initial search.
Search restrictions were human subjects, English language, peer-reviewed journal, RCTs and articles published up to February 2013.
Search
The search string used for this systemic review was: (low back pain OR back pain) AND (integrative care OR multidisciplinary care OR chiropractic OR spinal manipulation OR Chinese medicine OR traditional chinese medicine OR acupuncture OR homeopathy OR Ayurveda OR herbal medicine OR nutrition OR nutritional supplements OR mind-body medicine OR massage therapy OR yoga) AND (randomized controlled trial).
Study Selection
The three authors met together and reviewed each article to determine if each one met the predetermined inclusion criteria. Disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion and consensus and by performing a literature review on the meaning of integrated CAM therapies.
Data Collection Process
One author extracted the data from the articles into a spreadsheet. This was reviewed by a second author and disagreements between the authors resolved by consensus.
Data Items
Information that was extracted from the studies included:
Type of LBP
Sample size
Age of participants
Adverse events
Interventions used
Outcome measures
Results of interventions
Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
The Cochrane Back Review Group (CBRG) scale35 was used for rating the quality of the studies found (Table 1). All three authors rated each article independently and then met to discuss their ratings. When there was a disagreement the original article was reread until a consensus was formed. Articles that scored six points or more on the 12-point scale were rated as high-quality. Articles that scored less than six points should be rated as low-quality.35
Table 1.
The Cochrane Back Review Group Scale Questions
| Was the method of randomization adequate? | |
| Was the treatment allocation concealed? | |
| Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study? | Was the patient blinded to the intervention? |
| Was the care provider blinded to the intervention? | |
| Was the outcome assessor blinded to the intervention? | |
| Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed? | Was the dropout rate described and acceptable? |
| Were all randomized participants analyzed in the group to which they were allocated? | |
| Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting? | |
| Other sources of potential bias | Were the groups similar at baseline regarding the most important prognostic indicators? |
| Were co-interventions avoided or similar? | |
| Was the compliance acceptable in all groups? | |
| Was the timing of the outcome assessment similar in all groups? |
Planned Methods of Analysis
Data were extracted for the pain and disability effect estimates (between-group and/or within group differences) and for measures of variability (eg, confidence intervals) where possible. Clinical significance was determined using very minimal estimates based on existing literature.36-41 A statistician analyzed whether studies achieved clinically significant results. Statistical significance was reported for outcomes that did not have validated clinically significant cutoffs.
For this review, cutoffs were set at36-41:
> 10 mm on a 100-mm visual analog scale for pain (VAS)
> 10 points on Oswestry Low Back Pain Disability Questionnaire (Oswestry)
> 3 points on Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (Roland-Morris)
≥ 5 points on Short Form-36 (SF-36)
> 10 points on von Korff Scales (Pain and Disability)
> 5 points on Dartmouth Primary Care Cooperative chart system (COOP)
> 10 points on Aberdeen Low Back Pain Scale (Aberdeen)
> 2 points McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ)
> 1 on a 10-point Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS)
No further pooling of study results could be performed because of the heterogenicity of the outcome measures used.
Additional Analyses
The studies were grouped according to the modalities that were used in the treatment arms. Subgroup analysis was performed to determine the efficacy of the different integrative treatments for LBP. SMT was considered to be manual therapy delivered to correct spinal biomechanics. It could be applied by chiropractors, osteopaths, or physical therapists. Acupuncture could be provided alone or in conjunction with electrical stimulation applied directly to the needles. The points chosen could be traditional acupuncture points or muscle motor points or other points using neurological levels. Physiotherapy was considered any passive modality applied to the patient while exercise therapy was considered any active movement therapy to be performed by the patient.
The strength of the evidence for each group was calculated by looking at the degree of agreement on the effectiveness and the quality of the studies as determined by the CBRG score. The strength of the evidence was rated using a five-level scale to determine their place in the best evidence synthesis (Table 2).42
Table 2.
Best Evidence Synthesis Scale
| Level | Description | Evidence Required |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Strong evidence | More than 75% of high-quality RCTs report the same results |
| 2 | Moderate evidence | One high-quality RCT and/or multiple low-quality RCTs report the same results |
| 3 | Limited evidence | One low-quality RCT or one high-quality RCT and one low-quality RCT with opposite conclusion |
| 4 | Conflicting evidence | Contradictory results among multiple RCTs |
| 5 | No evidence | No RCTs |
Abbreviation: RCT, randomized controlled trial.
RESULTS
Study Selections
The search of PubMed, Medline, Index to Chiropractic Literature, Academic Search Premier, CINAHL, Cochrane Center Registry of Controlled Trials, and OVID provided total of 622 citations. Five hundred and ninety one of these articles were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria. The full text of the remaining 31 articles was obtained. The references of these articles were examined for any additional relevant studies and none were found. After review, nine of the 31 articles were excluded for not including an integrative CAM treatment arm or not including pain or disability outcome measures. One article was excluded because it was a duplicate. A total of 21 studies were found that met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
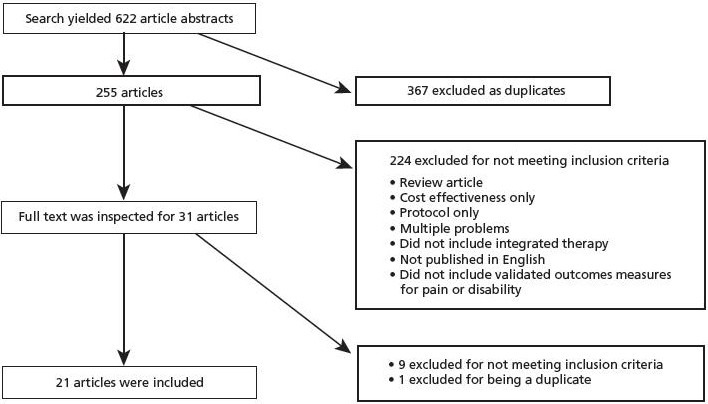
Flow of citations through the retrieval and screening process.
Study Characteristics
A total of 4400 patients were included in the 21 articles. Individual study sample sizes ranged from 32 to 1334. Two studies (10%) had fewer than 50 patients; five (24%) had between 50 and 100 patients, and 14 (67%) had more than 100 patients. Five studies (24%) included only acute LBP, 13 (62%) only subacute or chronic LBP (one of which specified patients with osteoarthritis in the low back), and three (14%) did not specify any chronicity (Table 3).
Table 3.
Study Characteristics
| Authors | Type of LBP | Sample size | Age | Interventions | Outcome Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beyerman et al, 200647 | Secondary to osteoarthritis (chronic) | 252 | Not reported | TG: SMT + Moist heat | Lumbar spine range of motion Oswestry VAS |
| CG: Moist heat | |||||
| Bronfort et al, 200845 | Chronic (≥6 weeks) | 174 | 20-60 y | TG: SMT + Strengthening exercise | VAS Roland-Morris COOP |
| CG: Conventional medical care + Strengthening exercise | |||||
| CG: SMT + stretching exercise | |||||
| Childs et al, 200443 | Not reported | 131 | 18-60 y | TG: SMT + Exercise | Oswestry |
| CG: Exercise | |||||
| Eisenberg et al, 200762 | Acute | 444 | 18 y and over | TG: Conventional medical care + Choice of acupuncture, chiropractic or massage therapy | NRS Roland-Morris Self-generated satisfaction scale Cost |
| CG: conventional medical care | |||||
| Gunn et al, 198060 | Chronic | 56 | 25-56 y | TG: Acupuncture (dry needling) + Conventional medical care | Self-generated pain and work status questionnaire |
| CG: Conventional medical care | |||||
| Hancock et al, 200751 | Acute | 240 | Not reported | TG: SMT + Conventional medical care | VAS for number of days to recovery |
| CG: Conventional medical care + Placebo SMT | |||||
| CG: SMT + Placebo conventional medical care | |||||
| CG: Placebo SMT + Placebo conventional medical care | |||||
| Hurley et al, 200448 | Sub-acute | 240 | 18-65 y | TG: SMT + Electric muscle stimulation | Roland-Morris VAS MPQ EQ-5D SF-36 Self-generated questionnaire for LBP recurrence, work absenteeism, exercise participation, analgesic medication consumption, and additional healthcare use |
| CG: SMT | |||||
| CG: Electric muscle stimulation | |||||
| Hurwitz et al, 200249 | Not reported | 341 | 18 years and overy | TG: SMT with physiotherapy modalities | NRS for pain Roland-Morris |
| CG: SMT | |||||
| Itoh et al, 200957 | Chronic | 32 | 61-81 y | TG: Acupuncture + TENS | VAS Roland-Morris |
| CG: Waiting list control | |||||
| CG: Acupuncture | |||||
| CG: TENS | |||||
| Jüni et al, 200950 | Acute | 104 | 20-55 y | TG: Conventional medical care + SMT | NRS Analgesic use |
| CG: Conventional medical care | |||||
| Leibing et al, 200256 | Chronic | 131 | 18-65 y | TG: Acupuncture + Active physiotherapy | VAS Pain Disability Index |
| CG: Active physiotherapy | |||||
| CG: Sham acupuncture + Active physiotherapy | |||||
| Mayer et al, 200561 | Acute | 122 | 18-55 y | TG: Heat-wrap therapy + Exercise | Rating of perceived capacity-spine |
| CG: Heat-wrap therapy | |||||
| CG: Exercise | |||||
| CG: Control (booklet) | |||||
| Meng et al, 200358 | Chronic | 55 | 60 y and over | TG: Acupuncture + Conventional medical care | Roland-Morris |
| CG: Conventional medical care | |||||
| Mohseni-Bandpei et al, 200644 | Chronic | 120 | 18-55 y | TG: SMT + Exercise | VAS Oswestry Lumbar spine range of motion Surface electromyography Lumbar extension muscle endurance |
| CG: Ultrasound + Exercise | |||||
| Molsberger et al, 200259 | Chronic | 186 | 20-60 y | TG: Acupuncture + Conventional orthopedic therapy | VAS Self-generated effectiveness of treatment Lumbar spine range of motion |
| CG: Conventional orthopedic therapy | |||||
| CG: Sham acupuncture + Conventional orthopedic therapy | |||||
| Niemistö et al, 200353 | Chronic | 204 | 24-46 y | TG: SMT + Stabilizing exercise + Conventional medical care | VAS Oswestry Frequency of LBP |
| CG: Conventional medical care | |||||
| Ongley et al, 198752 | Chronic | 81 | 21-70 y | TG: Forceful SMT + Injection of dextrose-glycerine-phenol into soft tissues + High dose of anesthesia | VAS Analgesic use Roland-Morris Adverse events |
| CG: Low dose of anesthesia + Less forceful SMT + Placebo injection | |||||
| UK BEAM Trial 200446 | Not reported | 1,334 | 18-65 y | TG: SMT + exercise | Roland-Morris Von Korff scales Back beliefs questionnaire Fear avoidance belief questionnaire SF -36 EQ-5D |
| CG: Conventional medical care | |||||
| CG: Exercise | |||||
| CG: SMT | |||||
| Weiner et al, 200863 | Chronic | 65 | 65 y and over | TG: Acupuncture (percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation [PENS]) + General conditioning and aerobic exercise (GCAE) | MPQ Roland-Morris |
| CG: PENS | |||||
| CG: Sham PENS | |||||
| CG: Sham PENS + GCAE | |||||
| Yeung et al, 200355 | Chronic | 52 | 18-75 y | TG: Exercise + Electro-acupuncture | NRS Aberdeen |
| CG: Exercise | |||||
| Zhang et al, 200854 | Acute | 36 | Not reported | TG: SMT + Biofreeze topical application | VAS Roland-Morris Low back muscle surface electromyography Heart rate variability |
| CG: SMT | |||||
Abbreviations: CG, control group; COOP, Dartmouth Primary Care Cooperative chart system; EQ-5D, European Quality of Life; LBP, low back pain; MPQ, McGill Pain Questionairre; NRS, numeric rating scale; SF-12 & 36: Short Form 12 & 36; SMT, spinal manipulative therapy; TENS, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation; TG, treatment group.
Eleven studies (52%) were limited to middle-aged participants. Three (14%) of the studies only included seniors, five studies (24%) included middle-aged and senior participants and two studies (10%) did not specify the age of the participants.
The modalities used in the studies included: SMT (13), conventional medical care (8), acupuncture (8), exercise (8), physiotherapy (5), massage therapy (1), topical application (1).
No studies were found that used integrated therapies that included homeopathy, Ayurveda, herbal medicine, nutrition, nutritional supplements, mind-body medicine, or yoga.
Risk of Bias Within Studies
The risk of bias within studies was determined using the CBRG scale (Table 4). Seventeen of the 21 studies (81%) were judged to be of high and four (19%) of low-quality. The most common problems encountered were lack of blinding of the participants, providers, and outcome assessors. Only eight of the studies reported on the use of any co-interventions by the participants and six on the participant's compliance with the treatment protocol.
Table 4.
The Cochrane Back Review Group Scores
| Randomization Adequate | Treatment Allocation Concealed | Patient Blinded | Care Provider Blinded | Outcome Assessor Blinded | Drop-Out Rate | Intention to Treat | Selective Outcome Reporting | Groups Similar at Baseline | Co-interventions | Compliance | Timing of the Outcomes | Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beyerman, 200647 | ? | – | – | – | – | + | – | + | + | ? | ? | + | 4 |
| Bronfort, 200845 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 9 |
| Childs, 200443 | + | + | – | – | – | – | + | + | + | ? | + | + | 7 |
| Eisenberg, 200762 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | 8 |
| Gunn, 198060 | + | + | – | – | ? | + | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | 6 |
| Hancock, 200751 | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 11 |
| Hurley, 200448 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | ? | + | + | 8 | |
| Hurwitz, 200249 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | 7 |
| Itoh, 200957 | + | + | – | – | – | + | ? | + | + | ? | ? | + | 6 |
| Jüni, 200950 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | ? | + | + | + | 8 |
| Leibing, 200256 | – | – | ? | – | ? | – | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | 4 |
| Mayer, 200561 | + | + | – | – | – | + | – | + | + | ? | ? | + | 6 |
| Meng, 200358 | + | + | – | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | ? | + | 7 |
| Mohseni-Bandpei, 200644 | + | + | – | – | + | – | + | ? | + | + | ? | + | 7 |
| Molsberger, 200259 | + | + | ? | – | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | 7 |
| Niemistö, 200353 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | + | ? | + | 8 |
| Ongley, 198752 | + | + | + | – | + | ? | – | + | + | ? | ? | + | 7 |
| UK Beam, 200446 | + | + | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | ? | – | + | 4 |
| Weiner, 200863 | + | + | ? | ? | ? | + | + | + | + | ? | + | + | 8 |
| Yeung, 200355 | + | + | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | ? | ? | + | 7 |
| Zhang, 200854 | + | + | – | – | – | ? | ? | + | + | ? | ? | + | 5 |
+, yes (1 point); –, no (0 points); ?, unclear (0 points).
Results of Individual Studies
A wide range of outcome measures were used in the studies included in this systematic review (Table 5). All of the outcome measures included were validated except Gunn et al,60 who used a self-generated questionnaire. Some studies reported only the within-group changes over time while others only reported between-group differences. Seventeen studies (81%) used primary outcome measures for pain or disability due to LBP. Even this consistency was confounded by the use of many different instruments that purport to measure the same outcome. Other primary outcome measures used included lumbar range of motion, satisfaction with care, prescription medication use, surface electromyography (EMG), lumbar muscle endurance, quality of life, perceived capacity of spine, adverse events, and heart rate variability.
Table 5.
Study Outcomes
| Study Name | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beyerman, 200647 | Intervention | SMT + Moist Heat | Moist Heat | ||
| N | 143 | 109 | |||
| Oswestry mean ± SDb | 8.56 ± 7.10a | 12.82 ± 7.66a | |||
| VAS mean ± SDb | 2.55± 2.01a | 3.99± 2.23a | |||
| Bronfort, 200845 | Intervention | SMT + Strengthening Exercise | Conventional Medical Care + Strengthening Exercise | SMT + Stretching Exercise | |
| N | 71 | 52 | 51 | ||
| VAS mean ± SD | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | ||
| Roland-Morris | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | ||
| COOP | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | Mean not reporteda | ||
| Childs, 200443 | Intervention | SMT + Exercise | Exercise | ||
| N | 70 | 61 | |||
| Oswestry mean differences (95% CI) | 8.3 (2.4, 14.2)b,c | ||||
| Eisenberg, 2007 62 | Intervention | Conventional Medical Care + Choice of Acupuncture, Chiropractic or Massage Therapy | Conventional Medical Care | ||
| N | 300 | 150 | |||
| NRS mean change after treatment (IQ)b | –5 (–7,–3) | –4 (–7,–2) | |||
| Roland-Morris change | –9 (–15,–4) | –8 (–13,–2) | |||
| Gunn, 1980 60 | Intervention | Acupuncture (Dry Needling) + Conventional Medical Care | Conventional Medical Care | ||
| N | 29 | 27 | |||
| Self-generated pain and work status b | Not reported | Not reported | |||
| Hancock, 2007 51 | Intervention | Conventional Medical Care + SMT + Diclofenac | Conventional Medical Care + Placebo SMT + Diclofenac | Conventional Medical Care + SMT + Placebo Diclofenac | Conventional Medical Care + Placebo SMT + Placebo Diclofenac |
| N | 60 | 60 | 59 | 60 | |
| Treatment Modality | Diclofenac | Placebo Diclofenac | SMT | Placebo SMT | |
| Days | 13 (10-16) | 16 (14-18) | 15 (13-18) | 15 (12-19) | |
| Number of days to a full day of zero on the VAS ( 95% CI) | |||||
| Hurley, 2004 48 | Intervention | SMT | Electric Muscle Stimulation | SMT + Electric Muscle Stimulation | |
| N | 80 | 80 | 80 | ||
| Change in Roland-Morris mean (95% CI) | –4.53 (–5.7,–3.3)a | –3.56 (–4.8,–2.4)a | –4.65 (–5.8,–3.5)a | ||
| Change in VAS (mm) mean (95% CI) | –19.88 (–26.1,–13.7)a | –21.38 (–27.5,–15.2)a | –24.69 (–30.8,–18.6)a | ||
| Hurwitz, 2002 49 | Intervention | SMT | SMT + Physiotherapy | ||
| N | 169 | 172 | |||
| Clinically significant Improvement on NRS (2 points/10) | 34.5% | 45% | |||
| Change in NRS (95% CI) | 1.04 (0.74, 1.35) | 1.35 (1.05, 1.66) | |||
| –0.31 (–0.13, 0.75) | |||||
| Clinically significant Improvement on Roland-Morris | 43.8% | 51.5% | |||
| Change in Roland-Morris (95% CI) | 3.18 (2.48, 3.88) | 3.16 (2.46, 3.86) | |||
| 0.02 (–1.02,0.97) | |||||
| Itoh, 2009 57 | Intervention | Acupuncture + TENS | No Specific Treatment | Acupuncture | TENS |
| N | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | |
| VAS mean ± SD | 36.6 ± 8.0a | 53.1 ± 27.9 | 37.4 ± 25.8 | 53.2 ± 25.1 | |
| Roland-Morris mean ± SD | 7.3 ± 4.9a | 9.8 ± 0.8 | 5.4 ± 3.4 | 6.2 ± 3.4 | |
| Jüni, 2009 50 | Intervention | Conventional Medical Care + SMT | Conventional Medical Care | ||
| N | 52 | 52 | |||
| 11-point Box scale for pain mean difference (95% CI) | 0.6 (–0.1, 1.3) | ||||
| Analgesic dose mean difference (95% CI) | –13 (–42, 15) | ||||
| Leibing, 2002 56 | Intervention | Acupuncture + Active Physiotherapy (AG) | Active Physiotherapy (CG) | Sham Acupuncture + Active Physiotherapy (SG) | |
| N | 40 | 46 | 45 | ||
| –2.7 ± 2.2 | –1.0 ± 1.7 | –2.1 ± 2.2 | |||
| Change in VAS mean ± SD | Contrast | Difference in Change in VAS Mean (95% CI) | |||
| AG vs SG | –0.6 (–1.65, 0.45) | ||||
| AG vs CGb,c | –1.7 ( –2.71,–0.62) | ||||
| –13.9 ± 15.0 | –2.6 ± 7.8 | –9.7 ± 10.5 | |||
| Change in pain disability index (PDI) mean ± SD | Contrast | Difference in Change in PDI (95% CI) | |||
| AG vs SG | –4.2 (–9.99, 1.71) | ||||
| AG vs CGb,c | –11.3 ( –17.01,–5.44) | ||||
| Mayer, 2005 61 | Intervention | Heat-Wrap Therapy + Exercise | Heat-Wrap Therapy | Exercise | Control (Booklet) |
| N | 24 | 25 | 25 | 26 | |
| Rating of Perceived Capacity-Spine (RPC-S) | Treatment Contrast | Relative Increase | |||
| Heat + Exercise vs Heatb | 84% | ||||
| Heat + Exercise vs Exerciseb | 95% | ||||
| Heat + Exercise vs Bookletb | 175% | ||||
| Meng, 2003 58 | Intervention | Acupuncture + Conventional Medical Care | Conventional Medical Care | ||
| N | 31 | 24 | |||
| Change in Rolland Morris questionnaire b,c | 4.1 ± 3.9a | 0.7 ± 2.8 | |||
| Mohseni-Bandpei, 2006 44 | Intervention | SMT + Exercise | Ultrasound + Exercise | ||
| N | 60 | 60 | |||
| Change in VAS (95% CI) | 41.6 (4.2, 49.6)a | 25.1 (17.7, 32.5)a | |||
| 16.4 (6.1, 26.8)b,c | |||||
| Change in Oswestry (95% CI) | 17.9 (14.0, 21.8 )a | 10.1 (6.2, 13.9)a | |||
| 7.8 (2.4, 13.2)b | |||||
| Molsberger, 2002 59 | Intervention | Acupuncture + Conventional Orthopedic Therapy (AC) | Conventional Orthopedic Therapy (C) | Sham Acupuncture + Conventional Orthopedic Therapy (SC) | |
| N | 65 | 60 | 61 | ||
| VAS mean ± SD | 26 ± 21 | 39 ± 21 | 36 ± 19 | ||
| 77% (62%, 88%) | 14% (4%, 30%) | 29% (16%, 46%) | |||
| VAS 50% pain relief (95% CI) | Contrast | ||||
| AC vs SCb,c | Difference in means not reported | ||||
| AC vs Cb | Difference in means not reported | ||||
| Niemist ӧ, 2003 53 | Intervention | SMT + Stabilizing Exercise + Conventional Medical Care | Conventional Medical Care | ||
| N | 102 | 102 | |||
| VAS mean ± SDb,c | 25.2 ± 23.3a | 36.1 ± 23.3a | |||
| Oswestry mean ± SDb | 14.7 ± 11.6a | 18.6 ± 11.6a | |||
| % with daily LBP | 37%a | 39%a | |||
| Ongley, 1987 52 | Intervention | Forceful SMT + Injection of Dextrose-Glycerine-Phenol into Soft Tissues + High-dose Anesthesia | Low Dose Anesthesia + Less Forceful SMT + Placebo Injection | ||
| N | 40 | 40 | |||
| VAS mean ± SD b,c | 1.77 ± 0.22 | 2.93 ± 0.25 | |||
| Roland-Morris b,c | 4.70 ± 0.73 | 8.49 ± 1.04 | |||
| UK BEAM Trial, 2004 46 | Intervention | General Practice (GP) | Exercise (E) | SMT (S) | SMT + Exercise (SE) |
| N | 338 | 310 | 353 | 333 | |
| Roland-Morris mean difference | Contrast | Mean difference (95% CI) | |||
| GP vs Eb | 1.36 (0.63, 2.10) | ||||
| GP vs Sb | 1.57 (0.82,2.32) | ||||
| GP vs SEb | 1.87 (1.15,2.60) | ||||
| Von Korff scales mean difference | Contrast | Mean difference (95% CI) | |||
| GP vs Eb | 5.03 (1.02,9.05) | ||||
| GP vs S | .97 (-0.050,7.98) | ||||
| GP vs SEb | 5.51 (1.75,9.28) | ||||
| Von Korff scales mean difference for pain | Contrast | Mean difference (95% CI) | |||
| GP vs Eb | 4.59 (0.43,8.75) | ||||
| GP vs Sb | 8.90 (4.84,12.95) | ||||
| GP vs SEb | 8.21 (4.20,12.21) | ||||
| Weiner, 2008 63 | Intervention | Acupuncture with PENS (A) | Acupuncture with PENS + Exercise (AE) | Acupuncture with sham PENS (S) | Acupuncture with Sham PENS + Exercise (SE) |
| N | 47 | 45 | 48 | 44 | |
| –2.9 ± 9.2a | –4.1 ± 8.2a | –2.3 ± 6.3a | –3.1 ± 7.9a | ||
| MPQ mean ± SD | Contrast | Mean ± SD | |||
| A vs S | 0.5 ± 1.4 | ||||
| AE vs SE | –0.6 ± 1.5 | ||||
| AE vs A | –1.4 ± 1.4 | ||||
| SE vs S | –0.3 ± 1.4 | ||||
| –2.6 ± 4.5a | –2.6 ± 4.6a | –2.7 ± 3.8a | –3.0 ± 4.7a | ||
| Roland-Morris mean ± SD | Contrast | Mean ± SD | |||
| A vs S | 0.1 ± 0.9 | ||||
| AE vs SE | 0.2 ± 0.9 | ||||
| AE vs A | –0.2 ± 0.9 | ||||
| SE vs S | –0.2 ± 0.9 | ||||
| Yeung, 2003 55 | Intervention | Exercise | Exercise + Electro Acupuncture | ||
| N | 26 | 26 | |||
| NRS mean ± SD b,c | 5.12 ± 2.18 | 3.81 ± 2.10 | |||
| Aberdeen mean ± SD b,c | 30.82 ± 13.03 | 20.02 ± 10.47 | |||
| Zhang, 2008 54 | Intervention | SMT | SMT + Topical Application | ||
| N | 18 | 18 | |||
| Roland- Morris questionnaire mean ± SD | 3.600 ± 5.412 | 8.000 ± 3.807 | |||
| VAS mean ± SD | 5.2 ± 2.167 | 1.333 ± 1.732a | |||
Significant within-group difference at P=.05.
Significant between-groups difference at P=.05.
Clinically significant between-groups difference.
Abbreviations: CG, control group; COOP, Dartmouth Primary Care Cooperative chart system; EQ-5D, European Quality of Life; LBP, low back pain; MPQ, McGill Pain Questionairre; NRS, numeric rating scale; SF-12 & 36: Short Form 12 & 36; SMT, spinal manipulative therapy; TENS, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation; TG, treatment group.
Some authors used multiple VAS for pain, such as current, average, and most severe pain. To simplify analysis, we used only average pain for this systematic review when multiple VAS scores for pain were reported.
When authors reported outcomes at multiple time points we chose to only include those taken at the conclusion of the intervention period.
Synthesis of Results
Studies were organized by the type of modalities used for treating LBP, the quality of the studies based on the CBRG score and whether the treatment was clinically effective. Levels of best evidence (Table 6) were calculated for each type of treatment using methods described above.
Table 6.
Best Evidence Synthesis
| Modalities Used | Clinically Effective | Clinically Not Effective | Level of Best Evidence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of Study | High | Low | High | Low | |
| SMT and Exercise | Childs, 200443 Mohseni-Bandpei, 200644 | UK BEAM, 200446 | Bronfort, 200845 | Clinically effective level 2 | |
| SMT and Physiotherapy | Beyerman, 200647 | Hurley, 200448 Hurwitz, 200249 | Clinically not effective level 2 | ||
| SMT and Conventional Medical Care | Ongley, 198752 | Jüni, 200950 | Clinically not effective level 4 | ||
| Hancock, 200751 | |||||
| SMT, Exercise and Conventional Medical Care | Niemistö, 200353 | Clinically effective level 2 | |||
| SMT and Topical Ointment | Zhang, 200854 | Clinically not effective level 3 | |||
| Acupuncture and Exercise | Yeung, 200355 | Leibing, 200256 | Weiner, 200863 | Clinically effective level 3 | |
| Acupuncture and Physiotherapy | Itoh, 200957 | Clinically not effective level 3 | |||
| Acupuncture and Conventional Medical Care | Gunn, 198060 Meng, 200358 Molsberger, 200259 | Clinically effective level 1 | |||
| Exercise and Physiotherapy | Mayer, 200561 | Clinically effective level 2 | |||
| Conventional Medical Care with Choice of Acupuncture, Chiropractic, or Massage | Eisenberg, 200762 | Clinically not effective level 3 | |||
Quality as measured on Cochrane Back Review Group scale: High, ≥6; Low, < 6.
Abbreviation: SMT, spinal manipulative therapy.
Spinal Manipulative Therapy and Exercise
A total of four studies were identified in this category. All of these studies were pragmatic trials, and all or most participants received SMT that included high-velocity thrusts. Childs et al43 and Mohseni-Bandpei et al44 had physiotherapists performing the SMT, Bronfort et al45 used chiropractors, and the UK BEAM trials46 used chiropractors, osteopaths, and physiotherapists. The UK BEAM46 study reported no adverse effects while Bronfort et al45 reported adverse effects mainly from NSAIDs. Childs et al43 and Mohseni-Bandpei et al44 did not report if there were any adverse effects. All trials except for Bronfort et al45 reported clinically effective results from the integrated therapy. Of the three high-quality studies,43-45 Childs et al43 and Mohseni-Bandpei et al44 reported that integrative treatments were more effective than the comparison therapy, leading to a level 2 best evidence score for using the integrated therapy.
Spinal Manipulative Therapy and Physiotherapy
A total of three studies were identified in this category. The Beyerman et al47 participants all had chronic LBP due to osteoarthritis. The Hurley et al48 participants had subacute LBP and the Hurwitz et al49 study did not specify the chronicity of the participants' LBP. The Hurley et al48 and Hurwitz et al49 studies were pragmatic, while the Beyerman et al47 participants all received a prescribed treatment regime. All three studies included a mix of high-velocity, low-amplitude thrusts and mobilization. Beyerman et al47 and Hurwitz et al49 used chiropractors to deliver the SMT, while Hurley et al48 used physiotherapists. Beyerman et al47 used moist heat as the physiotherapy, Hurley et al48 used electric muscle stimulation, and Hurwitz et al49 used the above plus cold and ultrasound. No adverse events were reported by any of these studies. The Beyerman et al47 study found that the integrated therapy was clinically effective; however, the two high-quality studies in this group, Hurley et al48 and Hurwitz et al,49 did not find a clinically significant effect for the integrative therapies, leading to a level 2 best evidence score against using the integrated therapy.
Spinal Manipulative Therapy and Conventional Medical Care
A total of three studies were identified in this category. The Jüni et al50 and Hancock et al51 participants had chronic LBP, while Ongley's52 had acute LBP. Ongley et al52 reported using only forceful SMT. The practitioner type was not reported. Jüni et al50 and Hancock et al51 reported using a mix of high-velocity, low-amplitude thrusts, and mobilization. The Hancock et al51 study used SMT performed by physiotherapists, while Jüni et al50 used a mix of different practitioner types. Hancock et al51 and Jüni et al50 reported adverse events. All three studies were high-quality. Ongley et al52 reported clinically significant effectiveness from the integrative therapy while the other two did not, leading to a level 4 best evidence score (conflicting evidence).
Spinal Manipulative Therapy, Exercise, and Conventional Medical Care
Only the Niemesto et al53 study was identified in this category. Participants all had chronic LBP. The SMT used was mobilization using a muscle energy technique. They did not report which profession performed the SMT. No adverse effects were reported by any of the participants. This high-quality study found that the integrated treatment was effective, leading to a level 2 best evidence score for using the integrated therapy.
Spinal Manipulative Therapy and Ointment
Only the Zhang et al54 study was identified in this category. The participants had acute LBP. The type of SMT performed was a diversified high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust performed by a chiropractor. A topical menthol ointment (Biofreeze, The Hygenic Corporation, Akron, Ohio) was applied by the participants. The occurrence of adverse events was not reported. There were no clinically significant effects observed from the treatments. This was a low-quality study and led to a level 3 best evidence score against using the integrated therapy.
Acupuncture and Exercise
Three articles were identified in this category. Participants all had chronic LBP. Yeung et al55 and Leibing et al56 used standardized acupuncture points, while Weiner et al63 used motor and other points according to a standardized program using neurological levels. All three studies applied electric stimulation to the needles. Yeung et al55 prescribed back-strengthening and stretching exercise, Leibing et al56 prescribed standardized active physiotherapy, and Weiner63 prescribed general conditioning and aerobic exercises. Yeung et al55 and Weiner et al63 reported no adverse events from the therapy, while Leibing et al56 reported pain and problems with circulation. Yeung et al55 and Leibing et al56 found this integrated therapy to be more effective than acupuncture alone, while Weiner et al found no difference between the integrated therapy and acupuncture or exercise therapy alone. The Yeung et al and Weiner et al studies were high-quality, while the Leibing et al study was low-quality, leading to a level 3 best evidence score (conflicting evidence).
Acupuncture and Physiotherapy
Only the Itoh et al57 article was identified in this category. The participants all had chronic LBP. The authors used a standardized set of acupuncture points for needling and applied transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) stimulation using pads separately from the needles. The only adverse event reported was deterioration of the symptoms in one participant. This study was high-quality and did not find the integrated therapy to be clinically effective. This led to a level 3 best evidence score against using this integrated therapy.
Acupuncture and Conventional Medical Care
Three studies that used integrated acupuncture and conventional medical treatments were found. All participants had chronic LBP. Meng et al58 and Molsberger et al59 used a standardized set of traditional acupuncture points with the option to choose additional points. Gunn et al60 chose to needle muscle motor points instead of traditional acupuncture points. Meng et al58 reported adverse events such as aches, bruises, light-headedness, and increased pain. Gunn et al60 and Molsberger et al59 did not report on the occurrence of adverse events. All three studies were high-quality and found that the integrated therapy was more effective than conventional medical care alone, leading to a level 1 best evidence score for using this integrated therapy.
Exercise and Physiotherapy
Only the Mayer et al61 study was found in this category. The participants all had acute LBP and received heat wrap therapy and McKenzie protocol exercises. No adverse events from the therapy were reported. This high-quality study found that the integrative therapy was clinically effective, leading to a level 2 best evidence score for using this integrated therapy.
Conventional Medical Care With Choice of Acupuncture, Chiropractic, or Massage
Only the Eisenberg et al62 study was found in this category. All patients had acute LBP. Of the participants in the treatment group, 51.4% chose massage therapy, 25.7% chose chiropractic, 19.6% chose acupuncture, and 3.4% declined additional therapy. No details on the conduction of CAM therapies were provided by the authors. Adverse events reported included minor discomfort among 5% of those receiving acupuncture care, 8% of those receiving chiropractic care, and 7% of those receiving massage. This study, deemed high-quality by the CBRG scale, found that the integrative care was not clinically effective, leading to a level 3 best evidence score against using this integrated therapy.
DISCUSSION
LBP remains a vexing problem throughout the world, causing significant pain and disability. Many years of research into the optimal approach to treating LBP have failed to find an ideal solution for all cases. Most likely, various combinations of modalities will be necessary for the different populations of LBP.30,31 This systematic review set out to determine if an integrated approach including combinations of CAM therapies and conventional medical care would be more effective than single modality treatment for the management of LBP. Overall, the results of this systematic review indicate that integrated modalities seem to be effective for this condition.
Twenty of the 21 studies included acupuncture and/or SMT. This is probably due to these modalities being used commonly to treat LBP and the more advanced state of the research communities in the professions that use these interventions.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine Combined With Conventional Medical Care
The combination of conventional medical therapy and CAM modalities appears to be the most promising approach to the management of chronic cases of this complex condition. A consensus among three high-quality trials that used acupuncture and conventional medical integrated therapy found it to be more effective for the management of chronic LBP than conventional medical care alone.58-60 However, none of these studies compared the integrated therapy with acupuncture alone. Future studies are required to determine if this integrated therapy is better than acupuncture alone. There were also no studies found on the use of this integrated therapy for acute LBP.
Combining conventional medical therapy and SMT led to conflicting evidence depending on the chronicity of the LBP. Two high-quality studies used participants with acute LBP and did not find that the integrated therapy was more effective than conventional medical care alone.50,51 One high-quality study used participants with chronic LBP and found that the integrated therapy was more effective than conventional medical therapy alone.52
The optimum management of acute LBP requires further study. In addition to the above studies, Eisenberg et al62 found that offering patients with acute LBP the choice of a CAM modality (acupuncture, chiropractic, or massage therapy) in addition to conventional medical care increased patient satisfaction and costs but did not improve outcomes. This may be due to the nature of acute LBP. In many cases it initially seems to resolve regardless of the therapy used, but there is high chance of recurrence. Long-term studies need to be performed to clarify which therapies are most effective in preventing future episodes.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine Combined With Active or Passive Care
Exercise has the advantages of being low risk, cost-effective approach that transfers responsibility for care to the patient. The addition of exercise to CAM therapies appears to be a promising approach to managing acute and chronic LBP. Five studies examined integrated therapy combining SMT and exercise. Of these, three high-quality43-45 and one low-quality study46 found that the integrated therapy was more effective than conventional medical therapy, physiotherapy, and exercise or exercise alone. One of these, Niemisto et al,53 combined conventional medical care, SMT, and exercise therapy. The Bronfort et al study45 had three groups which all received integrative therapy: SMT and strengthening exercise, SMT and stretching exercise, or conventional medical care with strengthening exercises. The three groups were all found to be equally effective, leading to the conclusion that SMT and strengthening exercise therapy was not more effective than the other two groups. However, the design of this study precludes coming to any conclusion about the effectiveness of integrated SMT and exercise compared to SMT or conventional medical therapy alone since all groups included some form of exercise.
Three studies55,56,63 addressed the use of integrated therapy including acupuncture and exercise therapy for chronic LBP. One high-quality55 and one low-quality56 study found that this integrated therapy was more effective than exercise alone or with sham acupuncture. Weiner et al63 did not find this integrated therapy to be more effective than acupuncture alone, but the participants in this study were all seniors aged 65 years or older, which may have impacted the outcomes.
While integrated CAM therapy with active care appears to be effective, combining passive physiotherapy modalities with CAM therapy was found to be generally ineffective.48,49,56,57 This was a surprising finding considering that this combination is often used as a standard treatment for LBP. This reinforces the modern paradigm that passive care alone may not be helpful in the management of LBP. On the other hand, combining active care with passive physiotherapy may be more effective as demonstrated by the Mayer et al61 study, which found that integrated therapy combining exercise with heat wrap was more effective than heat wrap or exercise alone or a control group. The authors described the participants of the study as having acute LBP, but the inclusion criteria specified that the condition had to have been present between 2 days and 3 months, which is commonly considered subacute.
Challenges of Integrated Care
There are some challenges to combining CAM modalities together or with conventional medical therapy. If multiple practitioners treat the same patients without coordinating care, there will be additional costs and time spent on each therapy, fragmentation of patient records, and duplication of services.8 There may also be an inconvenience to the patient if more than one clinic needs to be visited. These challenges can partially be mitigated by the increasing prevalence of multidisciplinary clinics, interprofessional collaboration and practitioners who can offer multiple therapies. For example, contemporary chiropractic and acupuncture education includes exercise therapy as part of their curriculum. Increased short-term costs may be justified if the integrated therapy leads to reduced chronic disability.
LIMITATIONS
One limitation was the large number of CAM modalities that could potentially be used in an integrated approach for LBP and the limited number of studies found. For several combinations of modalities, no articles could be identified. Among the integrated therapies that were included in this study, for each there were only one to four studies identified. This makes it impossible to draw a definitive conclusion regarding the most effective treatment for LBP. For example, even though every study except one used SMT or acupuncture treatment, no study was found that integrated these two therapies. In addition, the control group of many trials only included one of the interventions that were part of the integrated therapy. For example, all studies of integrated acupuncture and conventional medical care compared it to conventional medical care alone, but not to acupuncture alone.
Another limitation of this study was that only articles published in English were selected. This may have led to missing articles published in other languages. This is a particular concern for articles about acupuncture, which are often published in Chinese language journals.
Most of the studies included only participants who were described as having chronic LBP. Studies on LBP are often inconsistent when describing the chronicity categories of acute, subacute, chronic, and recurrent or do not describe this aspect at all. This may lead to uncertainty when attempting to translate research findings to clinical care. To add to the confusion, recent studies have pointed out that many cases of LBP that are originally considered acute and then resolved instead lead to recurrent LBP. Interventions that do not seem effective in the short-term may prove to be superior in preventing chronic recurrences and disability. Future studies should also explore the effects of integrated therapies on acute, chronic, and recurrent LBP. It is important for future studies to include long-term follow-up to determine if cases of LBP have truly resolved.
A limitation to combining results of the studies was the heterogeneity of the treatment modalities and outcomes used. For example, SMT delivered by chiropractors may differ significantly from that delivered by physical therapists. Some acupuncture trials used traditional points, while others used motor points. Numerous variations of pain and disability scales were used by the studies described in this article. In addition, Gunn et al60 used a self-generated LBP and disability questionnaire for the primary outcome measure, and Hancock et al51 used a VAS for pain in an unconventional manner for the primary outcome measure (number of days until zero is recorded).
One common concern for all studies of CAM modalities is that blinding of the patient and practitioner is often impossible. This combined with the common use of subjective pain and disability scales also led to the outcomes not being blinded. Despite this, 17 of the 21 studies scored in the high-quality range as determined by the CBRG scale.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients often try an integrated approach for treatment of LBP, using a combination of conventional medical care and CAM modalities. Previous systematic reviews have examined the use of individual CAM modalities for LBP and found promising results. This systematic review sought to determine if an integrated approach that includes different CAM therapies or CAM therapies combined with conventional medical care is more effective for the management of LBP than either alone. The studies found support the conclusion that integrated therapy which includes SMT combined with exercise therapy and acupuncture combined with conventional medical care or with exercise therapy appears to be more effective than select single therapies alone for treating LBP, although many questions remain. More studies are needed as most of the articles included participants with chronic LBP and there is a lack of RCTs for many CAM modalities used in an integrated manner. Further research into the integrated management of LBP is clearly needed to provide better guidance for patients and clinicians, as is the development of researchers with expertise in CAM modalities. In particular, there is a need for long-term studies that use cost effectiveness in addition to pain and disability from LBP as outcomes.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the help and support of Jeanette Duffels, Daniel Shen, and Drs Eric Hurwitz and Reed Phillips.
Disclosures The authors completed the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest and had no conflicts to report.
Footnotes
FUNDING No external funding was received for this review.
Contributor Information
Anupama Kizhakkeveettil, Southern California University of Health Sciences, Whittier, United States..
Kevin Rose, Southern California University of Health Sciences, Whittier, United States..
Gena E. Kadar, Southern California University of Health Sciences, Whittier, United States..
REFERENCES
- 1.Hart LG, Deyo RA, Cherkin DC.Physician office visits for low back pain. Frequency, clinical evaluation, and treatment patterns from a US national survey. Spine. 1995;20(1):11–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Walker BF.The prevalence of low back pain: a systematic review of the literature from 1966 to 1998. J Spinal Disord. 2000;13(3):205–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chou R, Qaseem A, Snow Vet al. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: a joint clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147(7):478–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Buchbinder R, Blyth FM, March LM, Brooks P, Woolf AD, Hoy DG.Placing the global burden of low back pain in context. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27(5):575–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoy D, Brooks P, Blyth F, Buchbinder R.The epidemiology of low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24(6):769–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S.A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and internationally. Spine J. 2008;8(1):8–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Savigny P, Kuntze S, Watson Pet al. Low back pain: early management of persistent non-specific low back pain. London, England: Royal College of General Practitioners (UK); 2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haldeman S, Dagenais S.A supermarket approach to the evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain. Spine J. 2008;8(1):1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Koes BW, van Tulder MW, Thomas S.Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. BMJ. 2006;332(7555):1430–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cherkin DC, Deyo RA, Wheeler K, Ciol MA.Physician views about treating low back pain. The results of a national survey. Spine. 1995;20(1):1–9; discussion 9-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Roelofs PDDM, Deyo RA, Koes BW, Scholten RJPM, van Tulder MW.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; (1):CD000396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chaparro LE, Furlan AD, Deshpande A, Mailis-Gagnon A, Atlas S, Turk DC.Opioids compared to placebo or other treatments for chronic low back pain: an update of the Cochrane Review. Spine. 2014April1; 39(7):556–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brumitt J, Matheson JW, Meira EP.Core stabilization exercise prescription, part 2: a systematic review of motor control and general (global) exercise rehabilitation approaches for patients with low back pain. Sports Health. 2013;5(6):510–513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Choi BK, Verbeek JH, Tam WW-S, Jiang JY.Exercises for prevention of recurrences of low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (1):CD006555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Van Tulder MW, Koes BW.Low back pain: chronic. Clinical evidence. London, England: BMJ Publishing Group; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SLet al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Furlan AD, Yazdi F, Tsertsvadze Aet al. Complementary and alternative therapies for back pain II. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2010; (194):1–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hirsch O, Strauch K, Held Het al. Low back pain patient subgroups in primary care—pain characteristics, psychosocial determinants and health care utilization. Clin J Pain. 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Furlan AD, van Tulder MW, Cherkin DCet al. Acupuncture and dry-needling for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; (1):CD001351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rubinstein SM, van Middelkoop M, Assendelft WJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW.Spinal manipulative therapy for chronic low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (2):CD008112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Furlan AD, Imamura M, Dryden T, Irvin E.Massage for low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; (4):CD001929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Furlan AD, Yazdi F, Tsertsvadze Aet al. Acupuncture for (sub)acute non-specific low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (8):CD009265. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Assendelft WJJ, Morton SC, Yu EI, Suttorp MJ, Shekelle PG.Spinal manipulative therapy for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; (1):CD000447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hayden JA, van Tulder MW, Malmivaara A, Koes BW.Exercise therapy for treatment of non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; (3):CD000335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gagnier JJ, van Tulder MW, Berman B, Bombardier C.Herbal medicine for low back pain: a Cochrane review. Spine. 2007;32(1):82–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Furlan AD, Imamura M, Dryden T, Irvin E.Massage for low back pain: an updated systematic review within the framework of the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine. 2009;34(16):1669–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rubinstein SM, Terwee CB, Assendelft WJJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW.Spinal manipulative therapy for acute low back pain: an update of the cochrane review. Spine. 2013;38(3):E158–177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rubinstein SM, van Middelkoop M, Assendelft WJJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW.Spinal manipulative therapy for chronic low-back pain: an update of a Cochrane review. Spine. 2011;36(13):E825–846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Frass M, Strassl RP, Friehs H, Müllner M, Kundi M, Kaye AD.Use and acceptance of complementary and alternative medicine among the general population and medical personnel: a systematic review. Ochsner J. 2012;12(1):45–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL.Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2008; (12):1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guzmán J, Esmail R, Karjalainen K, Malmivaara A, Irvin E, Bombardier C.Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: systematic review. BMJ. 2001;322(7301):1511–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Flor H, Fydrich T, Turk DC.Efficacy of multidisciplinary pain treatment centers: a meta-analytic review. Pain. 1992;49(2):221–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff Jet al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):W65–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.NCCAM. Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what's in a name? 2013. http://nccam.nih.gov/health/whatiscam AccessedAugust8, 2014.
- 35.Furlan AD1, Pennick V, Bombardier C, van Tulder M; Editorial Board, Cochrane Back Review Group. 2009 updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine. 2009;34(18):1929–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bombardier C, Hayden J, Beaton DE.Minimal clinically important difference. Low back pain: outcome measures. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(2):431–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chapman JR, Norvell DC, Hermsmeyer JTet al. Evaluating common outcomes for measuring treatment success for chronic low back pain. Spine. 2011;36(21 Suppl):S54–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Deyo RA, Dworkin SF, Amtmann Det al. Report of the NIH Task Force on research standards for chronic low back pain. Spine J. 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Garratt AM, Klaber Moffett J, Farrin AJ.Responsiveness of generic and specific measures of health outcome in low back pain. Spine. 2001;26(1):71–7; discussion 77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Maughan EF, Lewis JS.Outcome measures in chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(9):1484–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ostelo RWJG, Deyo RA, Stratford Pet al. Interpreting change scores for pain and functional status in low back pain: towards international consensus regarding minimal important change. Spine. 2008;33(1):90–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yuan J, Purepong N, Kerr DP, Park J, Bradbury I, McDonough S.Effectiveness of acupuncture for low back pain: a systematic review. Spine. 2008;33(23):E887–900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Childs JD, Fritz JM, Flynn TWet al. A clinical prediction rule to identify patients with low back pain most likely to benefit from spinal manipulation: a validation study. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141(12):920–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mohseni-Bandpei MA, Critchley J, Staunton T, Richardson B.A prospective randomised controlled trial of spinal manipulation and ultrasound in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Physiotherapy. 2006;92(1):34–42. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bronfort G, Haas M, Evans R, Kawchuk G, Dagenais S.Evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain with spinal manipulation and mobilization. Spine J. 2008;8(1):213–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.UK BEAM Trial Team. United Kingdom back pain exercise and manipulation (UK BEAM) randomised trial: effectiveness of physical treatments for back pain in primary care. BMJ. 2004;329(7479):1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Beyerman KL, Palmerino MB, Zohn LE, Kane GM, Foster KA.Efficacy of treating low back pain and dysfunction secondary to osteoarthritis: chiropractic care compared with moist heat alone. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2006;29(2):107–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hurley DA, McDonough SM, Dempster M, Moore AP, Baxter GD.A randomized clinical trial of manipulative therapy and interferential therapy for acute low back pain. Spine. 2004;29(20):2207–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hurwitz EL, Morgenstern H, Harber Pet al. Second prize: the effectiveness of physical modalities among patients with low back pain randomized to chiropractic care: findings from the UCLA low back pain study. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2002;25(1):10–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jüni P, Battaglia M, Nüesch Eet al. A randomised controlled trial of spinal manipulative therapy in acute low back pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(9):1420–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hancock MJ, Maher CG, Latimer Jet al. Assessment of diclofenac or spinal manipulative therapy, or both, in addition to recommended first-line treatment for acute low back pain: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9599):1638–43 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ongley MJ, Klein RG, Dorman TA, Eek BC, Hubert LJ.A new approach to the treatment of chronic low back pain. Lancet. 1987;2(8551):143–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Niemistö L, Lahtinen-Suopanki T, Rissanen P, Lindgren K-A, Sarna S, Hurri H.A randomized trial of combined manipulation, stabilizing exercises, and physician consultation compared to physician consultation alone for chronic low back pain. Spine. 2003;28(19):2185–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang J, Enix D, Snyder B, Giggey K, Tepe R.Effects of Biofreeze and chiropractic adjustments on acute low back pain: a pilot study. J Chiropr Med. 2008;7(2):59–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yeung CKN, Leung MCP, Chow DHK.The use of electro-acupuncture in conjunction with exercise for the treatment of chronic low-back pain. J Altern Complement Med. 2003;9(4):479–490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Leibing E, Leonhardt U, Köster Get al. Acupuncture treatment of chronic low-back pain—a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial with 9-month follow-up. Pain. 2002;96(1-2):189–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Itoh K, Itoh S, Katsumi Y, Kitakoji H.A pilot study on using acupuncture and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation to treat chronic non-specific low back pain. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2009;15(1):22–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Meng CF, Wang D, Ngeow J, Lao L, Peterson M, Paget S.Acupuncture for chronic low back pain in older patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42(12):1508–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Molsberger AF, Mau J, Pawelec DB, Winkler J.Does acupuncture improve the orthopedic management of chronic low back pain—a randomized, blinded, controlled trial with 3 months follow up. Pain. 2002;99(3):579–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gunn CC, Milbrandt WE, Little AS, Mason KE.Dry needling of muscle motor points for chronic low-back pain: a randomized clinical trial with long-term follow-up. Spine. 1980;5(3):279–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mayer JM, Ralph L, Look Met al. Treating acute low back pain with continuous low-level heat wrap therapy and/or exercise: a randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2005;5(4):395–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Eisenberg DM, Post DE, Davis RBet al. Addition of choice of complementary therapies to usual care for acute low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2007;32(2):151–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Weiner DK, Perera S, Rudy TE, Glick RM, Shenoy S, Delitto A.Efficacy of percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and therapeutic exercise for older adults with chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Pain. 2008;140(2):344–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


