Figure 2.
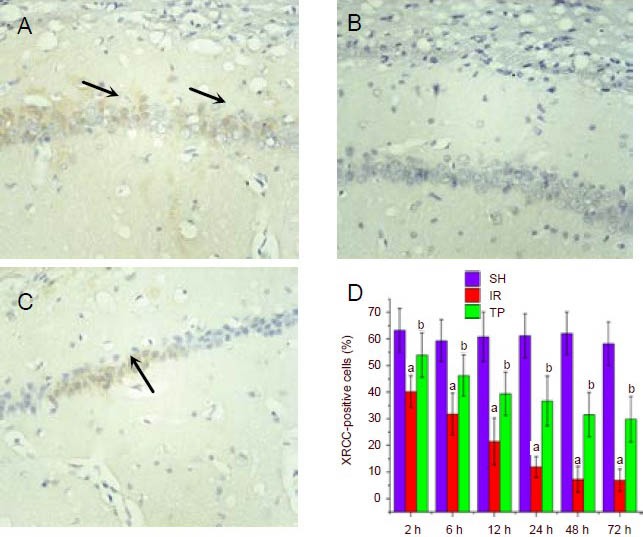
Tea polyphenols suppress the reduction in X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1) expression induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (immunohistochemistry staining, × 400).
Rats were treated as in Figure 1. Shown are representative XRCC1 immunohistochemistry figures from the hippocampal CA1 region at 48 hours for the SH group (A), IR group (B) and TP group (C). Arrows show XRCC1-positive cells.
D shows the percentage of XRCC1-positive cells from the three groups at different time points. Under ischemia/reperfusion injury, the percentage of XRCC1-positive cells decreased significantly from 2–72 hours (aP < 0.01, vs. SH group). Tea polyphenols suppressed the reduction in XRCC1 expression induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury (bP < 0.01, vs. IR group).
Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 6 per group per time point. Different groups were compared using analysis of variance for two-factor factorial design and least-significant difference t-test.
SH: Sham treated group; IR: ischemia/reperfusion group; TP: tea polyphenols group.
