Figure 3.
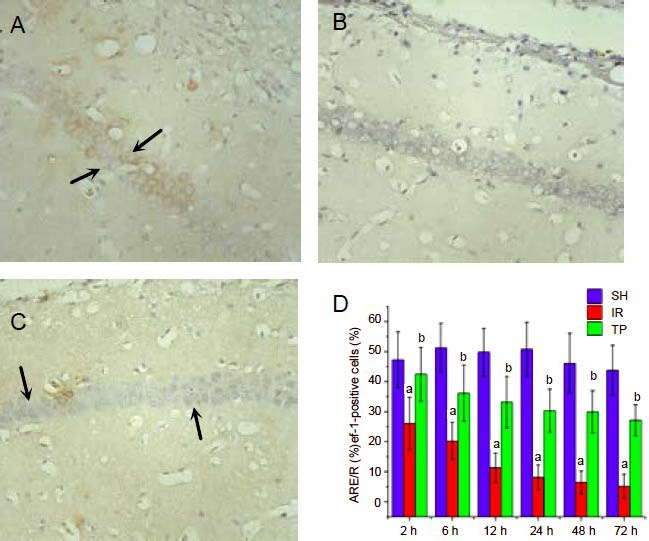
Tea polyphenols suppress the reduction in apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease/redox factor-1 (APE/Ref-1) expression induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (immunohistochemistry staining, × 400).
Rats were treated as in Figure 1. Shown are representative APE/Ref-1 immunohistochemistry figures from the hippocampal CA1 region at 48 hours for the SH group (A), IR group (B) and TP group (C). Arrows show APE/Ref-1-positive cells.
D shows the percentage of APE/Ref-1-positive cells from the three groups at different time points. Under ischemia/reperfusion injury, the percentage of APE/Ref-1-positive cells decreased significantly from 2- 72 hours (aP < 0.01, vs. SH group). Tea polyphenols suppressed the reduction in APE/Ref-1 expression induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury (bP < 0.01, vs. IR group).
Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 6 per group per time point. Different groups were compared using analysis of variance for two-factor factorial design and least-significant difference t-test.
SH: Sham treated group; IR: ischemia/reperfusion group; TP: tea polyphenols group.
