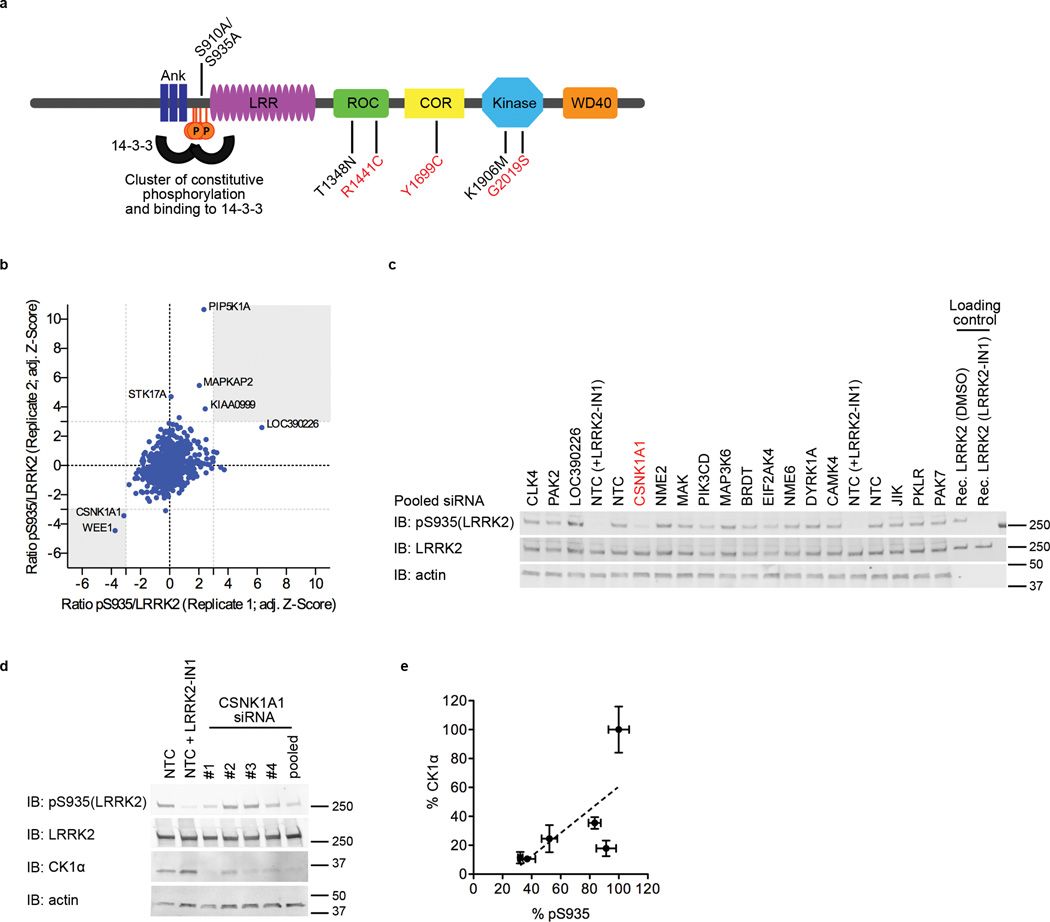
Figure 1. Casein kinase 1 alpha (CK1α) is a kinase regulator of LRRK2.
a) Schematic of the domain organization and location of LRRK2 constitutive phosphorylation sites. Domains include ankyrin (Ank), leucine-rich-repeat (LRR), Ras of complex proteins (ROC), C-terminal of ROC (COR), kinase and WD40 domains. Constitutive phosphorylation sites are clustered upstream of the LRR domain and crucial for binding to 14-3-3 proteins. Pathogenic mutations, shown in red (R1441C, Y1699C and G2019S; N1437S not shown), S910A/S935A, T1348N and K1906M, shown in black, are designed mutants used to block 14-3-3 binding, GTP/GDP binding and kinase activity respectively.
b) RNAi screen against kinases to identify kinase regulators of LRRK2 at S935. The screen was performed in duplicate per siRNA pool and each value of ratio pS935/LRRK2 was converted with a Z-transformation, adjusted for date of assay. Hits were identified if both replicates were 3 standard deviation Z away from mean. CSNK1A1 and WEE1 were two candidates with adjusted Z < −3.0 in both duplicates (bottom left grey box).
c) Western blot example from the RNAi screen identifying CSNK1A1 as the candidate kinase for S935 LRRK2. Recombinant LRRK2, purified from cells pre-treated with DMSO or LRRK2-IN1, were included in each blot as loading control to allow for normalization across blots.
d) CSNK1A1 validated using single siRNAs and pooled siRNAs. Three of four single CSNK1A1 siRNAs showed that when CK1α was knocked down, S935 phosphorylation was also reduced. Representative blots from 3 independent experiments. NTC – non-targeting control, single CSNK1A1 siRNAs - #1, 2, 3, 4 (used at 6.25nM final concentration).
e) Quantitation of blots in 1d. Graph shows mean +/− SEM (n=3) for relative CK1α and phosphorylated LRRK2 signals.