Figure 1. RA-9 is an inhibitor of 19S-associated DUBs.
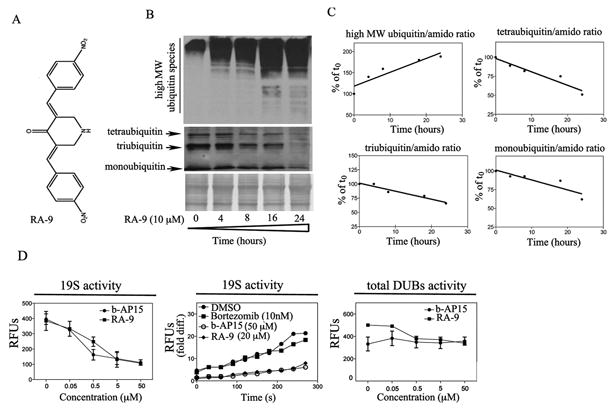
A, chemical structure of RA-9 (3E, 5E)-3,5-bis(nitrobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one. B, time-dependent accumulation of high-molecular weight ubiquitin species and concomitant reduction in mono, tri and tetraubiquitin species in ES-2 ovarian cancer cell line exposed to 10μM RA-9 for 4h, 8h, 16h and 24 h. Amido black staining was used as loading control. C, quantification of the ubiquitin/total protein (amido) ratio expressed as % of t0. D. Left panel, dose-dependent residual DUB activity in 19S RP exposed to the indicated doses of RA-9 expressed as Relative Fluorescence Units (RFUs). b-AP15 was used as positive control. Middle panel, time-dependent residual deubiquitinating enzyme activity in 19S proteasome particles exposed to the indicated dose of RA-9 expressed as fold Relative Fluorescence Units (RFUs) difference over time. b-AP15 was used as positive control. Bortezomib was used as negative control. Right panel, dose-dependent residual DUB activity in ES-2 cell lysate (total DUBs activity) exposed to the indicated doses of RA-9 expressed as Relative Fluorescence Units (RFUs). b-AP15 was used as positive control.
