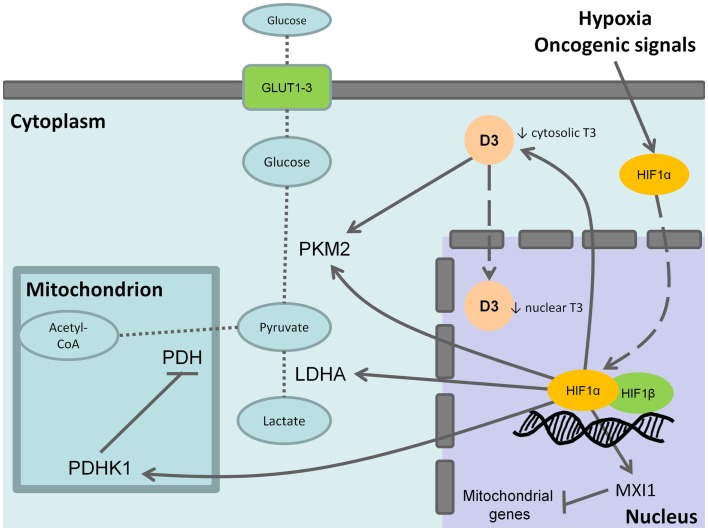
Figure 1.
Effects of type 3 deiodinase expression on Warburg phenotype. Hypoxia or oncogenic signals inhibit HIF-1a degradation and stabilize the nuclear association between HIF-1a and HIF-1b resulting in the transactivation of HIF-1 target genes. The activation of the M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), and of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDHK1) that, in turn, inhibits the mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) shunts cell metabolism from the mitochondrial respiration toward the fermentative glycolysis. Furthermore, the induction of max interactor 1 (MXI1), a transcriptional target of HIF-1 complex, inhibits mitochondrial biogenesis through the downexpression of nuclearly encoded mitochondrial genes. The coexpression of type 3 deiodinase (D3) decreases cytosolic triiodothyronine (T3) levels resulting in the activation of PKM2. It is also possible that D3 translocates from cytoplasm to the cell nucleus mediating nuclear thyroid hormone inactivation and local hypothyroidism. Bold arrows indicate activation, whereas the blunted lines indicate inhibition. Dashed arrows indicate protein translocation between cellular compartments. Dotted lines indicate the pathway reactions.