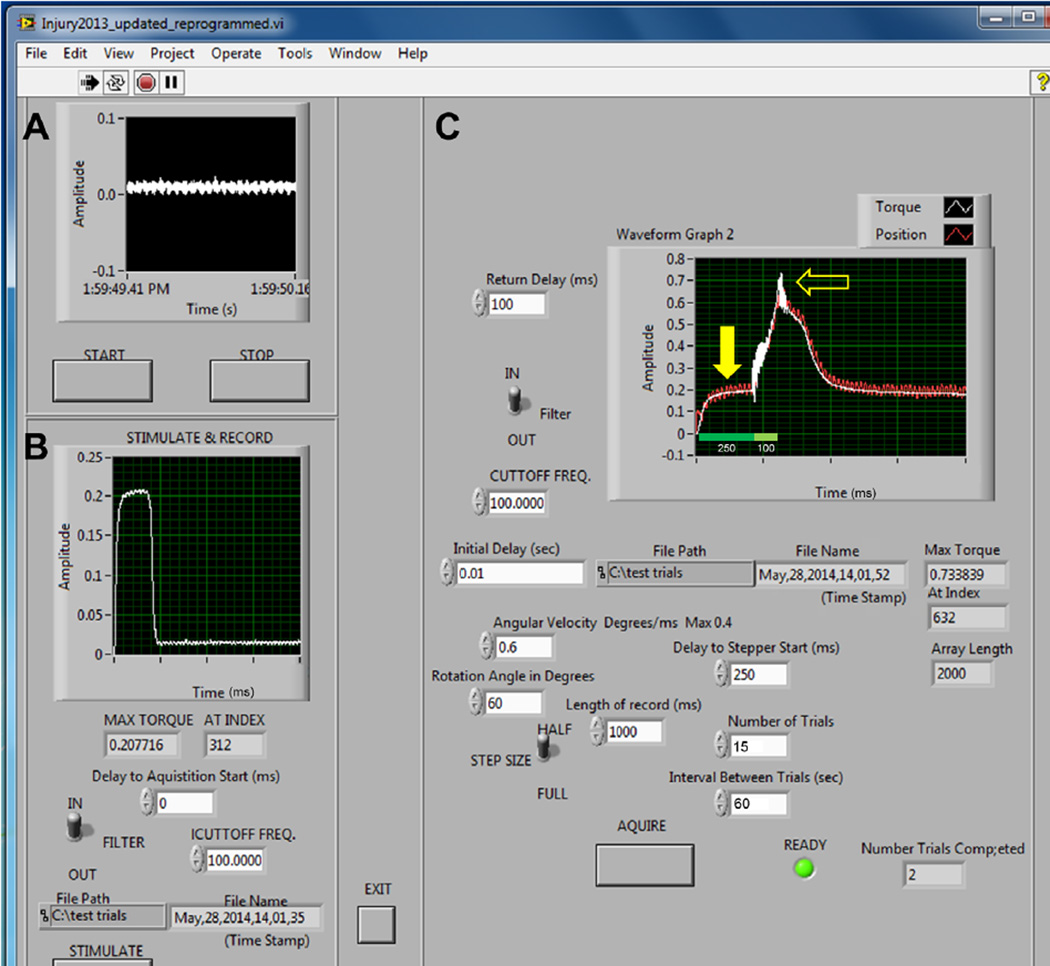
Figure 4. Torque data from in vivo apparatus.
A. Before experiments, the torque sensor can be tested for proper sensitivity/calibration and the baseline adjusted to zero. B. Once the animal is secured into the apparatus, maximal isometric torque is recorded from a fused tetanic contraction in the quadriceps before and after lengthening contractions. Maximal isometric torque is achieved using optimal muscle length, stimulation rate (Hz), and voltage (see step 5). C. Recordings from lengthening contractions show peak amplitude from a 250 ms train stimulation before onset of motor movement (closed arrow). Stimulation of the femoral nerve continues (an additional 100 ms) throughout forced flexion of the quadriceps via the motor driven lever arm. This produces a high force peak (closed arrow) during the lengthening contraction.