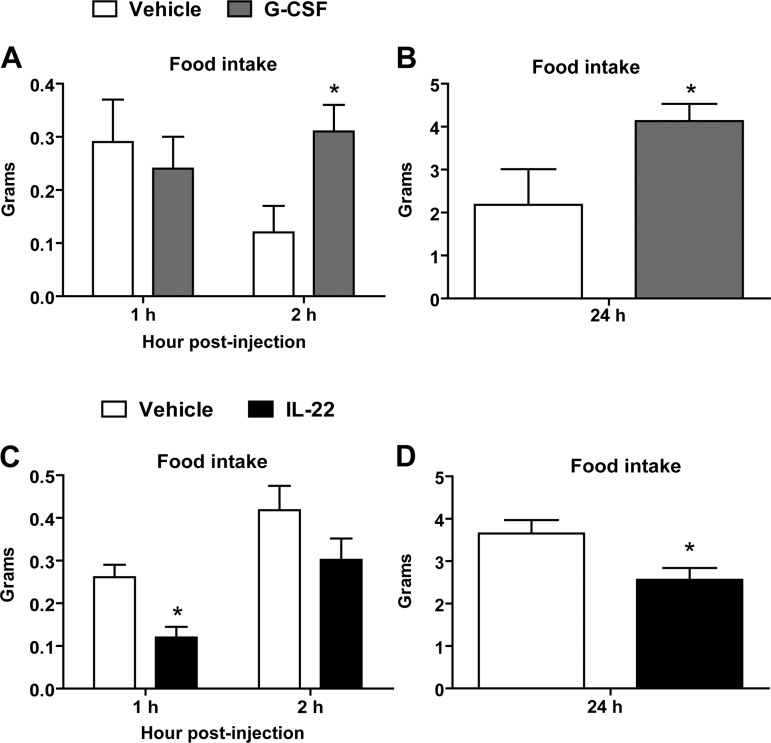
Fig. 3.
Alterations in food intake after central injection of G-CSF or IL-22. Intracerebroventricular administration of G-CSF increased food intake at 2 h (A) and 24 h (B). Central delivery of IL-22 decreased food intake at 1 h (C) and reduced cumulative food intake at 24 h (D). Data are shown as means ± SE (n = 8–10 for saline control; n = 6 for G-CSF; n = 5 for IL-22). *P < 0.05.