Fig. 4.
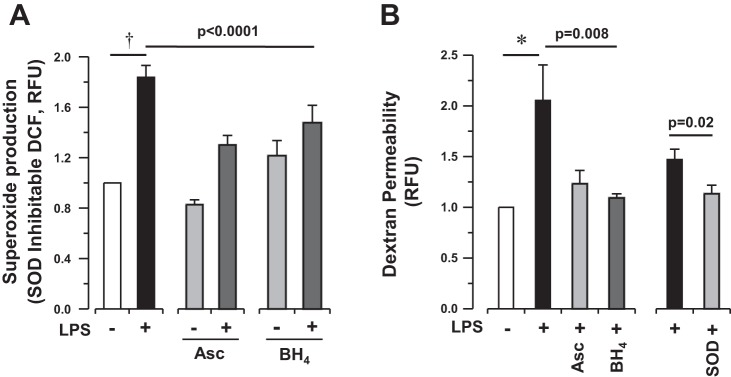
Bacterial LPS-induced superoxide production is associated with the development of barrier dysfunction in vitro. A: SOD-inhibitable DCF fluorescence in media extracted from HLMVEC following LPS exposure (1 μg/ml for 4 h) in the presence of ascorbate (500 μM) (Asc) or BH4 (50 μM). B: fluorescent dextran accumulation in basal media after apical exposure of HLMVEC to LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h) in the presence of ascorbate (500 μM), BH4 (50 μM), or SOD (50 U/ml). SOD experiment is shown separately, as it represents separate experiment with its own control cells. LPS-induced permeability is attenuated in the presence of antioxidants or superoxide-specific SOD. Bars represent means ± SE of n ≥ 12 individual experiments. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA (Asc and BH4) and Student's t-test (SOD). Post hoc analysis by Bonferroni test for superoxide production (A, Asc P = 0.002, BH4 P = 0.11) and for permeability (B, Asc P = 0.04, and BH4 P = 0.01). †P < 0.0001 and *P < 0.01 by 1-sided paired t-test.
