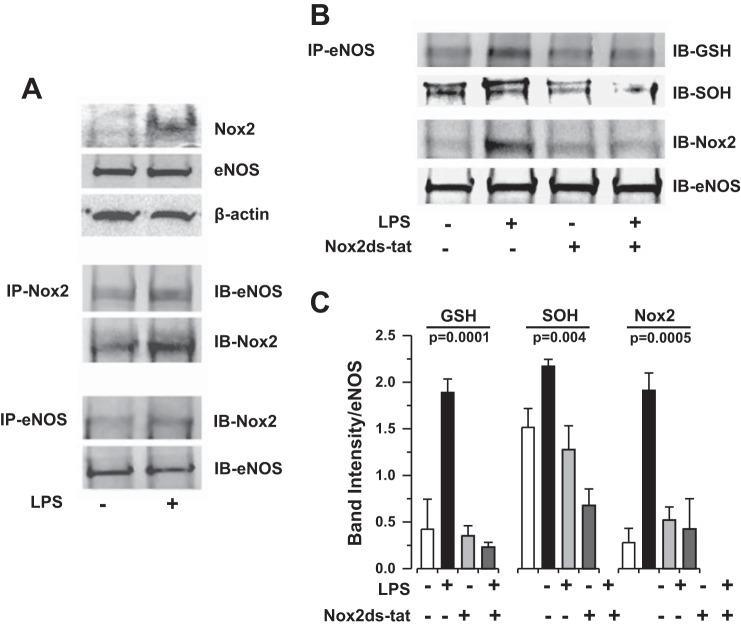
Fig. 8.
Bacterial LPS induces eNOS association with Nox2 and subsequent oxidative modification of eNOS enzyme in HLMVEC in vitro. A: coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) of eNOS and Nox2 protein in HLMVEC following LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h) exposure. Bacterial endotoxin induces an association of eNOS with Nox2 in HLMVEC in vitro. IB, immunoblotting. B: representative co-IP of eNOS protein with S-glutathionyl (GSH) and sulfenic acid (SOH) moieties following LPS (1 μg/ml for 4 h) exposure in the presence or absence of the Nox2-specific peptide inhibitor Nox2ds-tat (10 μM). C: densitometry quantification of n ≥ 3 individual co-IP experiments presented in B. Statistical analysis performed by 1-way ANOVA. LPS-induced oxidative modification of eNOS protein (S-glutathionylation and sulfenic acid formation) is dependent on Nox2.