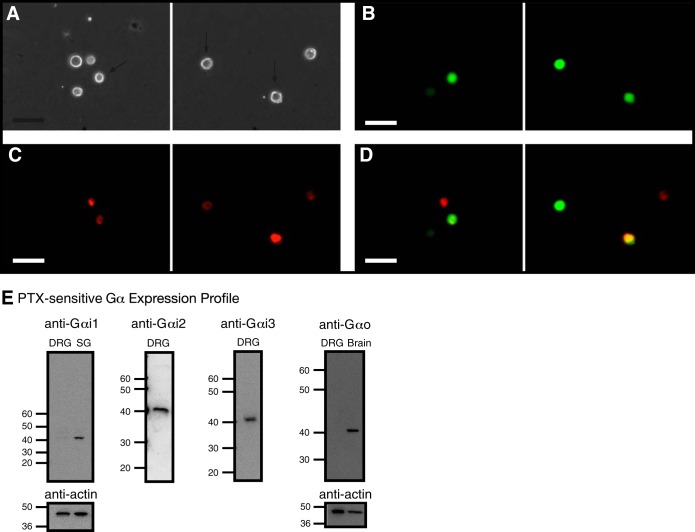
Fig. 2.
Fluorescence imaging of retrograde-labeled and enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter-microinjected cDNA in rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons and detection of pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive Gα subunit expression in DRG tissue. Phase (A) and fluorescence (B–D) images of acutely isolated DRG neurons, 5 days post-1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) injection in the triceps surae muscles and ∼18 h post-cDNA transfection. The neurons were imaged at 20×, with a filter set containing an excitation filter at 480 nm and an emission filter at 535 nm (for EGFP, B) and an excitation filter at 540 nm and an emission filter at 585 nm (for DiI, C). D: images represent color-joined images from B and C. The images were pseudocolored; scale bars represent 60 μm. The arrows (A) point to DiI-labeled and EGFP-expressing neurons. E: expression of Gα subunits in DRG tissue. Western blot assays showing the natively expressed Gα subunits. The blots used anti-Gαi1, -Gαi2, -Gαi3, -GαO, and -actin. Each lane was loaded with 20–25 μg protein. Gαi1 and GαO were not detected in DRG tissue but were present in stellate ganglion (SG) and brain tissue, respectively. The lines/numbers to the left of the blots indicate the approximate molecular masses (kDa).