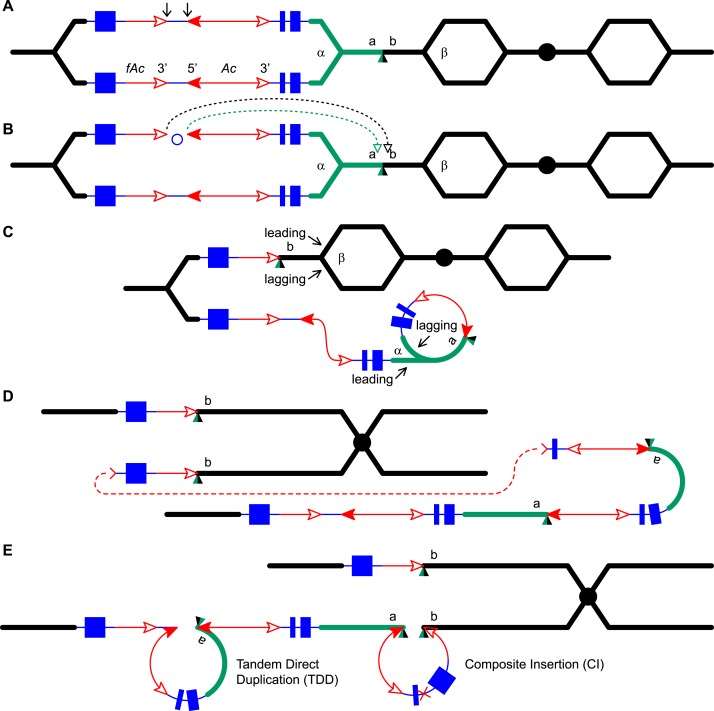
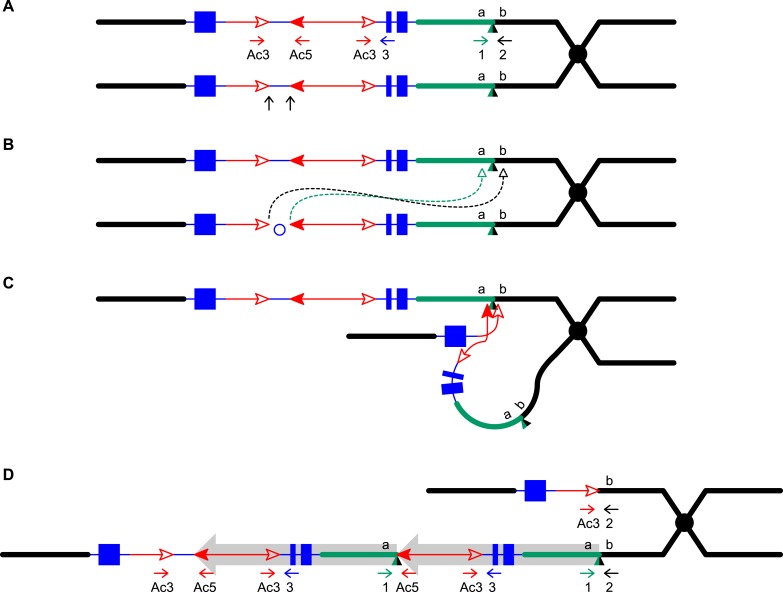
Figure 1. Reversed Ac ends transposition (RET) during DNA replication generates Tandem Direct Duplication (TDD) and Composite Insertion (CI).
Lines indicate a replicating chromosome, hexagons indicate replicons. The blue boxes are exons 1, 2, and 3 (right to left) of the p1 gene, and the green/black triangles are the transposition target site. Red lines with arrow(s) indicate Ac/fAc insertions, and the open and solid arrowheads indicate Ac/fAc 3′ and 5′ ends, respectively. Two replication forks considered here are marked α and β. For animated version, see Video 1. (A) The locus containing fAc/Ac is replicated. Vertical arrows indicate the sites of Ac transposase cuts at the fAc 3′ and Ac 5′ ends. (B) Transposase cleaves and the inter-transposon segment is ligated to form a circle. The excised transposon ends will insert into an unreplicated target site indicated as the green/black triangle. Like standard Ac/Ds transposition, insertion of the Ac/fAc termini into the target site generates an 8-bp target site duplication (TSD; green/black triangle). (C) Insertion of the excised transposon termini places fAc and fAc-flanking DNA ahead of replication fork β (upper chromatid), and Ac and Ac-flanking DNA ahead of replication fork α to generate a rolling circle replicon (lower chromatid). DNA replication continues. (D) Following re-replication of fAc, Ac, and a portion of the flanking sequences, DNA replication forks α and β stall and abort, resulting in chromatids terminated by broken ends (the red > or < symbol) (Michel et al., 1997). The dotted red line connects the two broken ends that will fuse together. (E) Chromatid fusion produces a chromosome with two unequal sister chromatids: The upper chromatid contains a deletion of the segment from fAc to the a/b target site. The lower chromatid contains a TDD (left-hand loop), as well as a new CI (right-hand loop). The TDD contains the DNA deleted from the upper chromatid; the CI contains the re-replicated Ac, fAc and flanking sequences. The junction where broken chromatid ends were joined is indicated by the red ×.