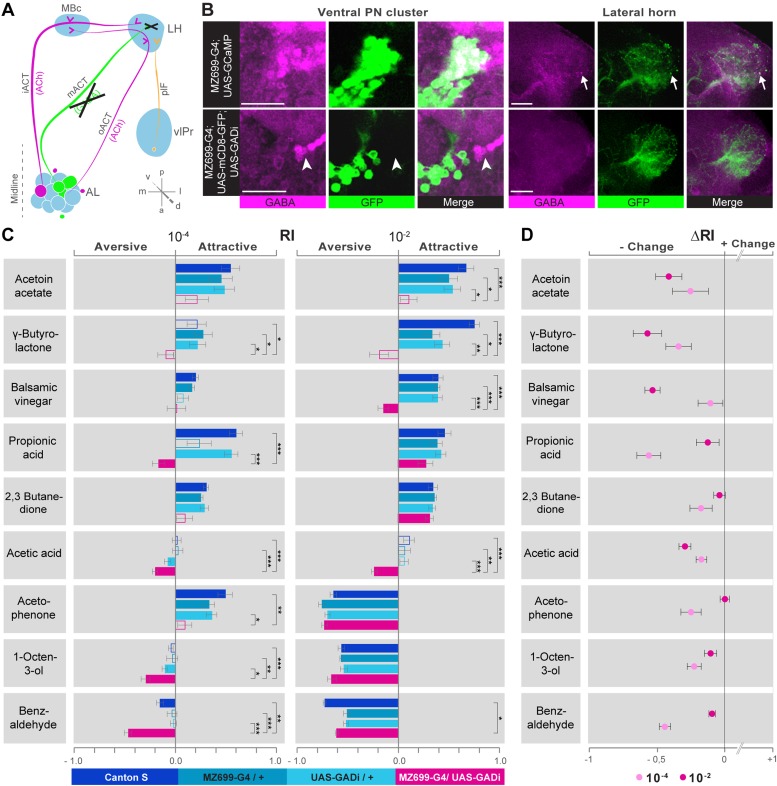
Figure 5. iPN GABA release in the LH mediates odor attraction behavior.
(A) Experimental layout: iPN GABA production was selectively silenced via GADi expression in MZ699+ iPNs; ePN and vlPr neuron activity remained unaffected. (B) Immunostaining against GABA and GFP within AL somata (left) and LH neurites (right) of iPNs with intact (top) and silenced GABA production (bottom). GADi flies show GABA signals in somata of iPNs labeled by GH146-GAL4 only (arrowhead). The arrow head points to an exemplary GABA-positive bouton in the LH. Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) Averaged behavioral response indices (RIs) determined with a T-maze assay for wild-type flies (dark blue), parental controls (light blue) and experimental animals (magenta) for nine odorants at two concentrations. Empty boxes display no response (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Dunn's Multiple Comparison Test was used for global differences in the dataset followed by a posthoc test for selected pairs (p* < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Error bars represent SEM. (D) RI differences between GADi flies and averaged parental controls. RI differences are negative for all but one odor indicating that GADi expression shifts odor-guided behavior towards aversion. Error bars indicate SEM.