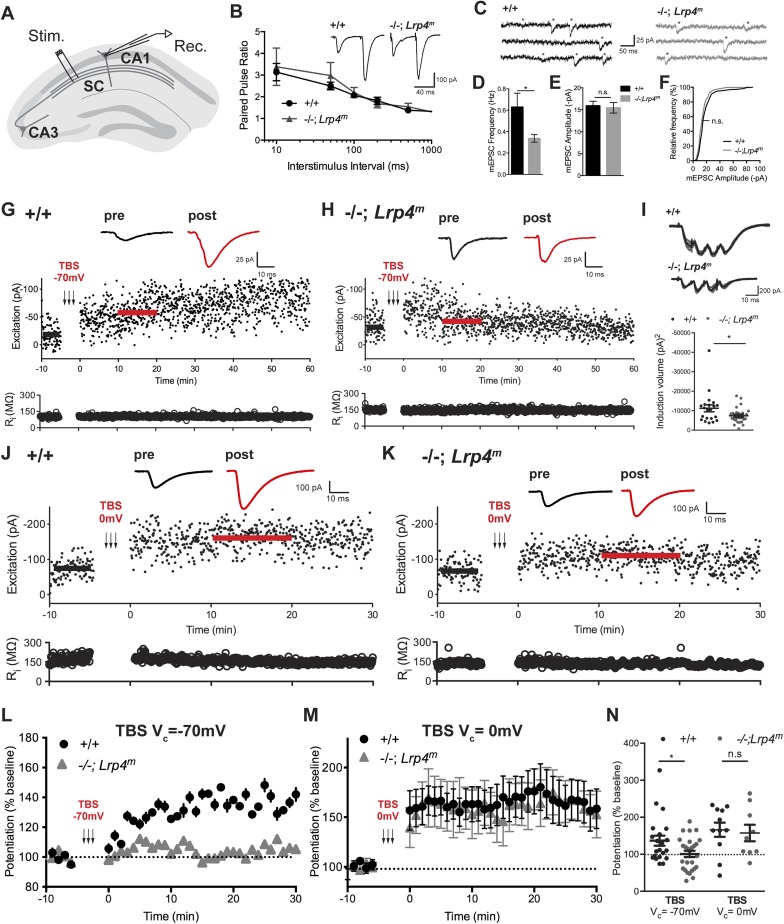
Figure 5. Lrp4 is required for normal synaptic transmission.
(A) The panel shows the configuration of whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings made from acute hippocampal slices of young, adult mice. Postsynaptic responses in CA1 pyramidal neurons were measured following stimulation of Schaffer collaterals (SC). (B) Representative traces from CA1 neurons to paired stimuli show that paired-pulsed facilitation is normal in Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m mice (wild-type, n = 9; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 6). (C) Representative traces of spontaneous miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSC) of wild-type or Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons. (D) mEPSC frequency is reduced in Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons (wild-type, n = 12; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 12. (E, F) mEPSC ampitudes of Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons are comparable to wild-type (wild-type, n = 12; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 12). (G, H) Representative traces from individual CA1 neurons following a TBS delivered to neurons, which were voltage-clamped at −70 mV, show LTP from wild-type but not Lrp4 mutant neurons (upper panel). Excitation, measured as the amplitude of an EPSC (pA), is shown below, and input resistance (Ri) is shown in the bottom panel. There is considerable variability in the baseline EPSC amplitudes in slices from wild-type and Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m mice. However, there was no significant difference in the baseline EPSC amplitudes between wild-type and mutant mice (wild-type, 52.6 ± 9.7 pA, n = 21; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, 44.9 ± 4.9 pA, n = 27, p = 0.44). Further, there was not a significant correlation between the magnitude of LTP and initial synaptic strength (wild-type, R2 = 0.05, n = 21, p = 0.35; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, R2 = 0.09, n = 21, p = 0.13). (I) Representative traces from individual CA1 neurons during TBS show a reduction in the integral of the summed EPCSs recorded during a single TBS in Lrp4-deficient neurons, top panel. Induction volume, quantified as the integral of the postsynaptic response, is shown in the bottom panel (wild-type, n = 21; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m; n = 32) (J, K) Representative responses from individual CA1 neurons following a TBS delivered to neurons, which were voltage-clamped at 0 mV, show a restoration of LTP in Lrp4 mutant neurons (upper panel). Excitation, measured as the amplitude of an EPSC (pA), is shown in the middle panel, and input resistance (Ri) is shown in the bottom panel. (L) Averaged data from control cells (n = 21) and Lrp4 mutant (n = 32) neurons shows that the response from wild-type neurons is potentiated 1.5-fold, whereas Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons potentiate little, if at all 30 min following a TBS delivered at Vc = −70 mV. (M) Depolarization of Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons during TBS restores LTP (wild-type, n = 11; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 9). (N) Quantitation of potentiation at 10-20 min after TBS demonstrates a lack of LTP in Lrp4 mutant CA1 neurons, which is restored upon depolarization (Vc = −70 mV: wild-type, n = 21; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 32; Vc = 0 mV: wild-type, n = 11; Lrp4−/−; Lrp4m, n = 9).