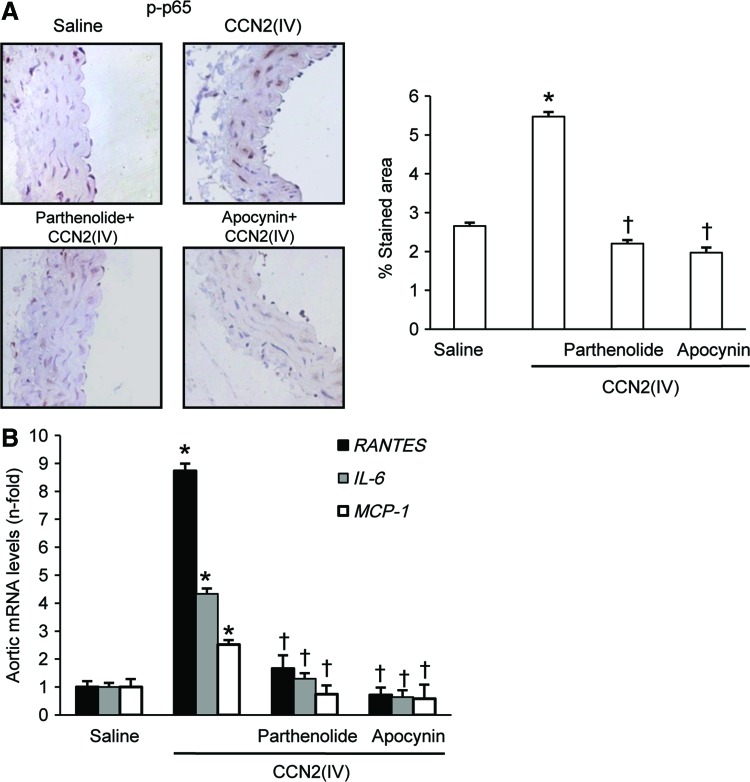
FIG. 6.
CCN2(IV) activates NF-κB via redox process in murine aorta. C57BL/6 mice received a single i.p. injection of 2.5 ng/g body weight recombinant CCN2(IV) or saline and were sacrificed after 24 h (n=10 mice per group). Some mice were pretreated with parthenolide (3.5 mg/kg of body weight; n=9) or apocynin (50 g/kg of body weight; n=8) 24 h before CCN2(IV) administration. NF-κB activation was determined by evaluation of phosphorylated p65 NF-κB immunostaining in paraffin-embedded aortic sections. (A) A representative immunostained section (left) and the quantification (right) of the immunostaining. (B) Gene expression of the proinflammatory factors (IL-6, MCP-1, and RANTES) was evaluated by real-time PCR in aorta from saline and CCN2(IV)-injected mice. Data are expressed as mean±SEM of fold increase over saline of 8–10 animals per group. *p<0.05 versus saline. †p<0.05 versus CCN2(IV). IL-6, interleukin-6; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; RANTES, regulated on activation normal T cell expressed and secreted. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars