Figure 3.
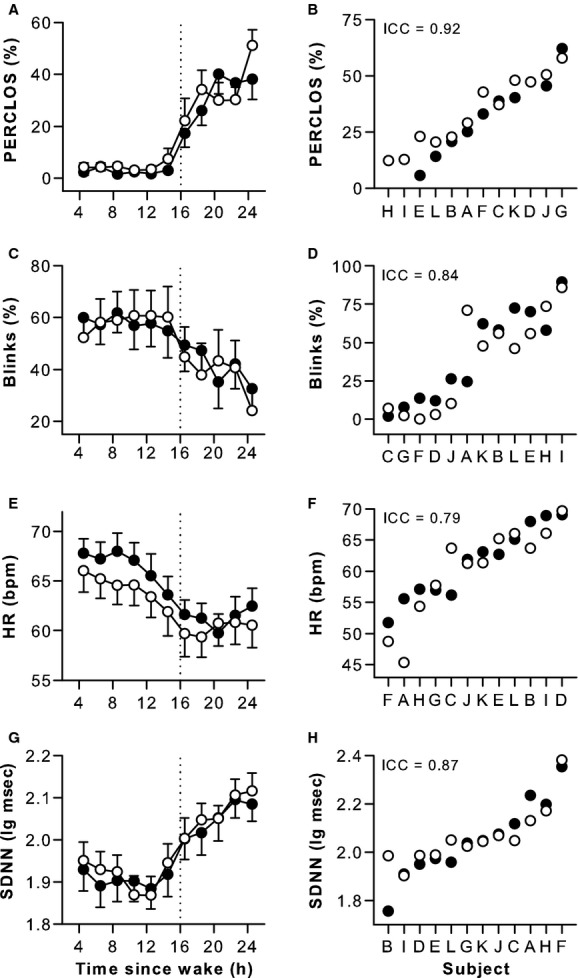
Individual differences in ocular and electrocardiogram measures during sleep deprivation were highly reproducible. As wakefulness was extended beyond usual bedtime, subjects closed their eyes a greater percentage of the time and blinked less frequently, and between‐subject differences were stable across exposures to sleep deprivation (A–D). During the usual hours of sleep, heart rate decreased and variability in heart rate increased, and differences in these measures were highly reproducible between subjects (E–H). Black circles show results for the first study visit, and open circles show results for the second study visit. In panels A, C, E, and G, the mean ± SEM is shown. In panels B, D, F, and H, subjects (n = 12, A–L) are ranked from left to right according to their average response across study visits, and the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) is shown at the top left of each plot. In three participants (D, H, and I), percentage eye closure was not assessed during the first study visit. PERCLOS, percentage eyelid closure over the pupil over time; HR, heart rate; bpm, beats per minute; SDNN, standard deviation of normal‐to‐normal RR intervals.
