Figure 3.
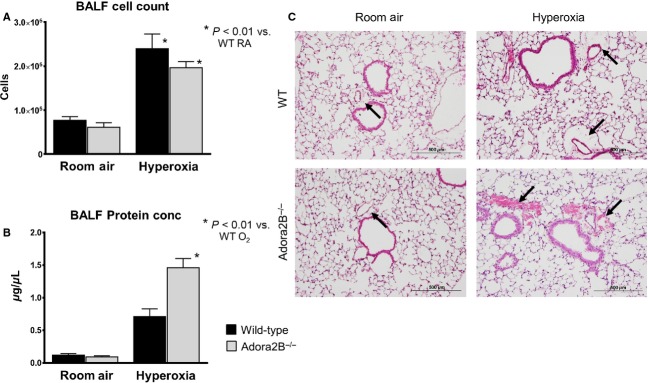
Loss of ADORA2B worsens pulmonary edema in hyperoxic lung injury. Adora2B−/− mice were exposed to room air or 95% oxygen environment for 72 h (n = 13 for room air, n = 14 for hyperoxia). Adora2B−/− mice had no change in BALF cell count in hyperoxia (A) but did have a significant elevation in BALF protein concentration (B) indicating worsened pulmonary edema. H&E staining of representative sections shows an increase in perivascular fluid accumulation in hyperoxia compared to room air that is exaggerated and demonstrates red blood cell extravasation in Adora2B−/− mice (black arrows) (C). Panels for wild‐type mice are the same as presented in Figure 2.
