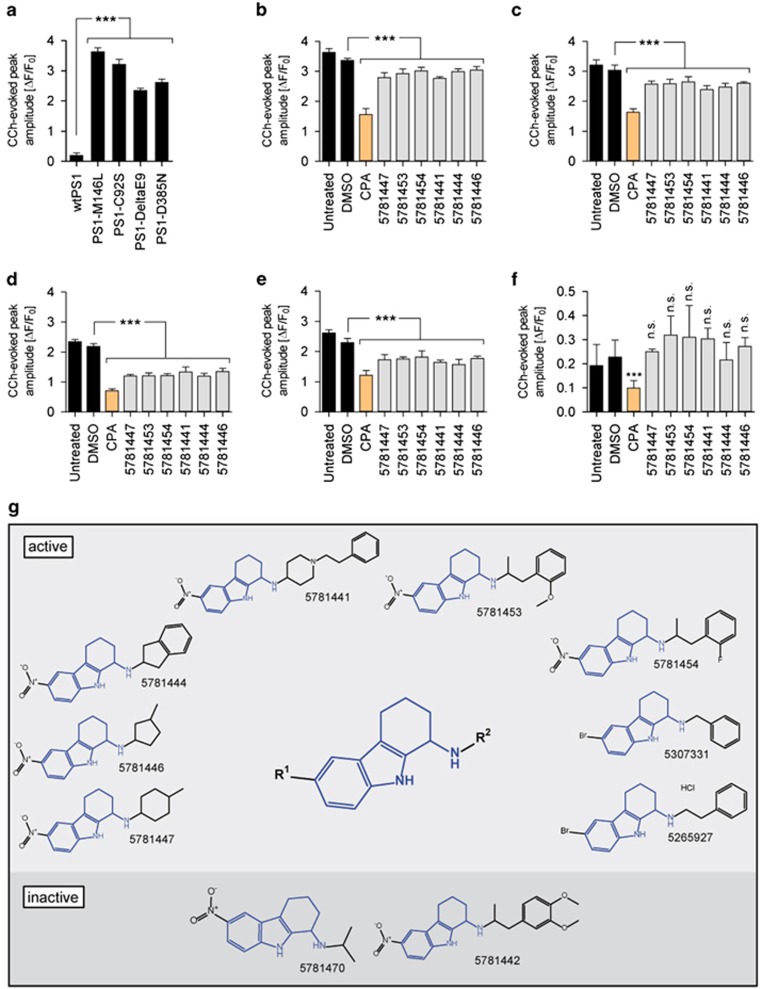
Figure 1.
Tetrahydrocarbazole analog screening hits/lead structure and their effects on FAD-PS1-mediated disrupted ER calcium release. (a) The peak amplitude of CCh-evoked calcium release in HEK293 cells expressing wild-type PS1, FAD-linked (PS1-M146L, PS1-C92S and PS1-DeltaE9) or a γ-secretase deficient (PS1-D385N) PS1 mutations. The effect of six tetrahydrocarbazole hits identified from the primary screen at 10 μM in (b) PS1-M146L, (c) PS1-C92S, (d) PS1-DeltaE9, (e) PS1-D385N and (f) wild-type PS1-expressing HEK293 cells on the peak amplitude of CCh-evoked calcium release. CPA, an inhibitor of calcium-dependent ATPases, was used as a positive control. (g) The tetrahydrocarbazole lead structure, identified from a high-throughput compound screen for substances normalizing the exaggerated CCh-evoked calcium release in PS1-M146L HEK293 cells. Illustrated are chemical structures of the 10 tetrahydrocarbazole analogs present in the entire screened compound library. The upper and lower panels indicate, respectively, eight active and two inactive analogs of the lead structure. Compounds capable of reducing the peak amplitude of CCh-induced calcium release to <90% of DMSO-treated controls (normalized ER calcium <0.9) were regarded as active hits. (n.s., non-significant; ***P<0.001; n=4). CCh, carbachol; CPA, cyclopiazonic acid; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FAD-PS1, familial Alzheimer's disease presenilin 1.