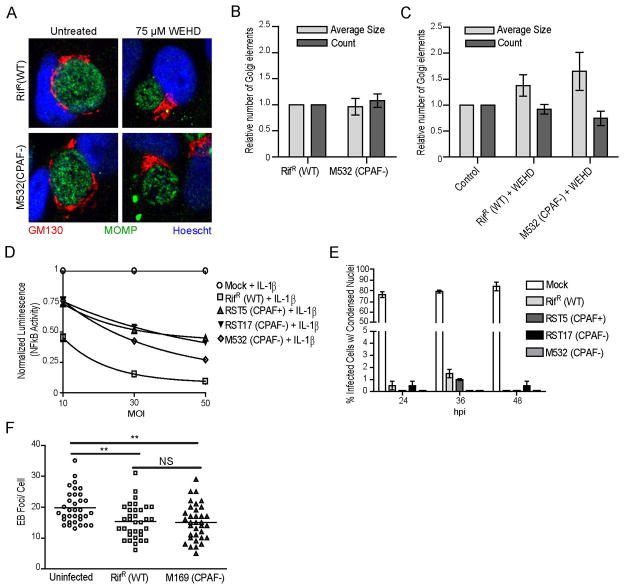
Figure 3. CPAF is not required for many of the cellular phenotypes associated with C. trachomatis infection.
A–C) C. trachomatis-induced Golgi fragmentation occurs in a z-WEHD-fmk-dependent manner in the absence of CPAF. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated strains for 24hpi and processed for immunofluorescence to visualize the Golgi apparatus (GM130, red), C. trachomatis, (MOMP, green) and DNA (Hoescht, blue). No difference was observed in Golgi fragmentation as assessed visually and by post-acquisition processing to assess size and number of Golgi elements between wild-type and a CPAF-deficient strain infections (panels A and B). In the same experiment, cells were treated with 75μM z-WEHD-fmk from 9hpi, which inhibited Golgi fragmentation in cells infected with wild-type and a CPAF-deficient strain (panels A and C). Three independent experiments, SEM. D) HeLa cells stably expressing an NFκB luciferase reporter were infected with the indicated strains at an MOI of 10, 30, or 50 for 24 hours and were simultaneously treated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β. Luciferase activity was measured in cell lysates and normalized to the treated mock-infected control. CPAF-deficient strains and RifR (WT) strains show an MOI dependent decrease in luciferase activity. E) Infected or mock-infected HeLa cells were treated with 2 μM staurosporine for 6 hours prior to the indicated time points and the percentage of infected cells with condensed nuclei determined. F) HeLa cells were either infected with the indicated strain or left uninfected for 29 hours prior to being infected at an MOI=25 with GFP-expressing LGV-L2 for 1 hour. The number of phospho-tyrosine foci per cell was determined for 35 cells. HeLa cells infected with the CPAF-deficient strain (M169) remain protected from superinfection. **: p < 0.01, SEM, n=3.