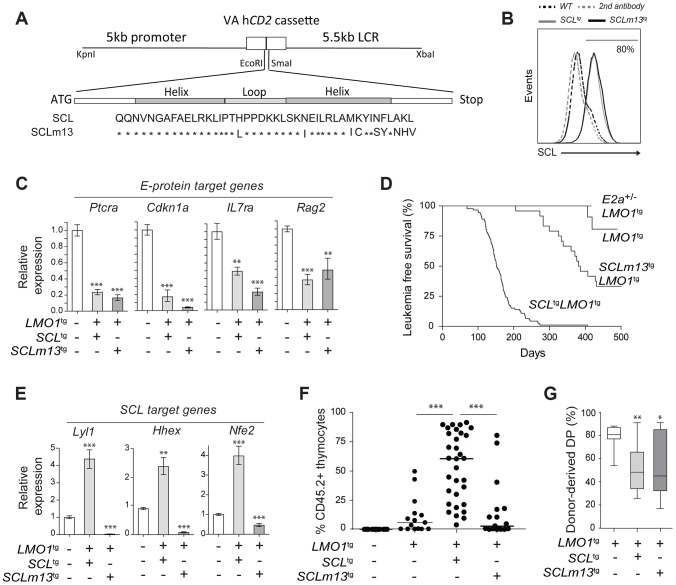
Figure 5. Transcription activation driven by SCL-LMO1 interaction is critical for thymocyte reprogramming and T-ALL induction.
(A) Generation of transgenic mice expressing the LMO1-binding defective mutant SCLm13. The sequence coding for wild type human SCL or human SCLm13 HLH domain mutant [37] were cloned into the VA hCD2 cassette to generate transgenic mice. Shown are amino acids of the HLH region of SCL or SCLm13. (B) Immunofluorescence of human SCL (wt or m13) by flow cytometry. Thymocytes were stained with the monoclonal antibody against human SCL (BTL73). Control cells were stained with the second antibody only. (C) Expression of E protein target genes is inhibited both by SCL-LMO1 and SCLm13-LMO1 transgenes in DN3 thymocytes. mRNA levels in purified DN3 thymocytes from the indicated transgenic mice were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to β-Actin (Mean +/- SD, n = 3). (D) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for LMO1tg, E2a+/-LMO1tg, SCLtgLMO1tg and SCLm13tgLMO1tg mice. (E) The interaction between SCL and LMO1 is required to activate the transcription of the self-renewal genes Lyl1, Hhex and Nfe2 in DN3 thymocytes. mRNA levels in purified DN3 thymocytes from the indicated transgenic mice were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to β-Actin (Mean +/- SD, n = 3). (F–G) SCL but not the LMO1-binding defective SCL-m13 mutant collaborates with LMO1 to induce abnormal thymic reconstitution potential to thymocytes. Pre-leukemic thymocytes (1.5×107 cells) from 3-week-old mice were transplanted. Recipient mice were analysed for thymic reconstitution (CD45.2+Thy1+) after 6 weeks (F) and the proportion of DP cells in engrafted CD45.2+Thy1+ thymocytes was assessed by FACS (G).