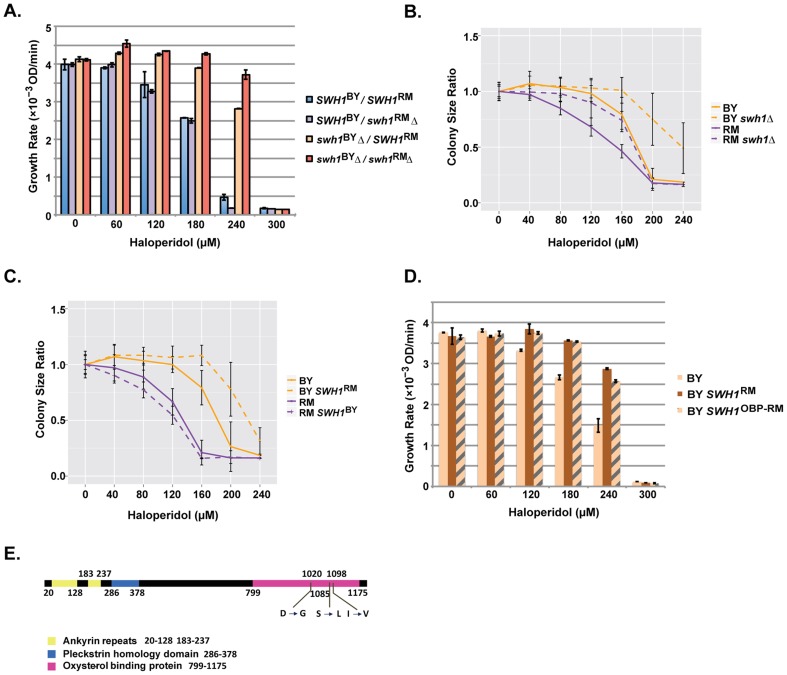
Figure 4. Polymorphisms in the OBP domain of SWH1 underlie haloperidol resistance.
(A) Reciprocal hemizygosity assay as well as double deletion analysis assessing the contribution of SWH1 and its allelic state in a BY/RM hybrid background. Growth curves were spline fitted to extract the maximum growth rates. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. The mean ±1 s.d. are plotted. (B) Comparison of swh1Δ relative to wild type BY and RM. Saturated cultures were spotted onto YPD agar plates supplemented with 0–240 µM haloperidol and plates were incubated at 30°C for ∼72 hr. Shown are colony size ratios obtained by normalizing colony sizes to those on YPD. Mean values ±1 s.d. are plotted. (C) Allele replacements of SWH1. Saturated cultures were spotted onto YPD agar plates supplemented with 0–240 µM haloperidol, plated were incubated at 30°C for ∼48 hr. Mean colony size ratio ±1 s.d. are plotted. (D) Replacing the SWH1 oxysterol binding protein like domain (OBP) in BY with the RM counterpart (OBP-RM) recapitulates the growth rates of replacing the entire SWH1 gene with the RM allele. (E) Three nonsynonymous SNPs reside in the oxysterol binding protein like domain (OBP) in SWH1.